Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Focus on the Manufacturing of New Ceramic Materials: Insights into Ceramic Structural Parts
1. Core Classification of New Ceramic Materials for Structural Parts
New ceramic materials for structural applications are categorized primarily by their chemical composition, each tailored to specific industrial demands based on inherent performance advantages.
Oxide Ceramics: Represented by zirconium oxide (ZrO₂) and aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), these materials excel in wear resistance, insulation, and mechanical strength. Zirconia stands out for its exceptional toughness, while alumina is valued for its cost-effectiveness and stable performance across general industrial scenarios .
Nitride Ceramics: Silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) and aluminum nitride (AlN) are prominent members, offering superior high-temperature stability and thermal conductivity. Silicon nitride’s resistance to thermal shock makes it ideal for extreme-temperature components, while aluminum nitride is favored in electronic thermal management applications .
Carbide Ceramics: Silicon carbide (SiC) leads this category with outstanding corrosion resistance and hardness, performing reliably in harsh chemical and high-wear environments .
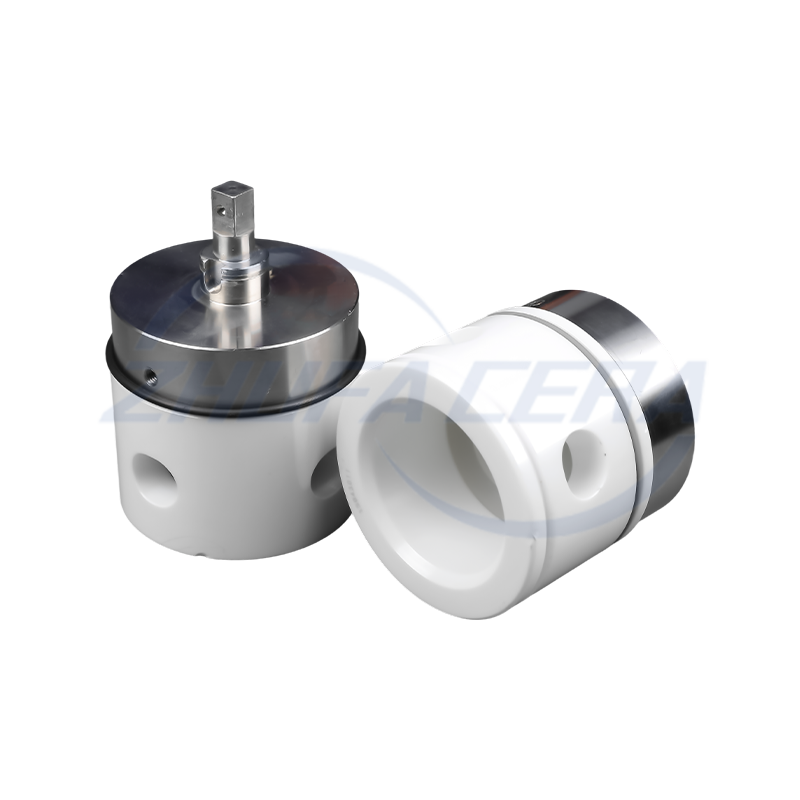
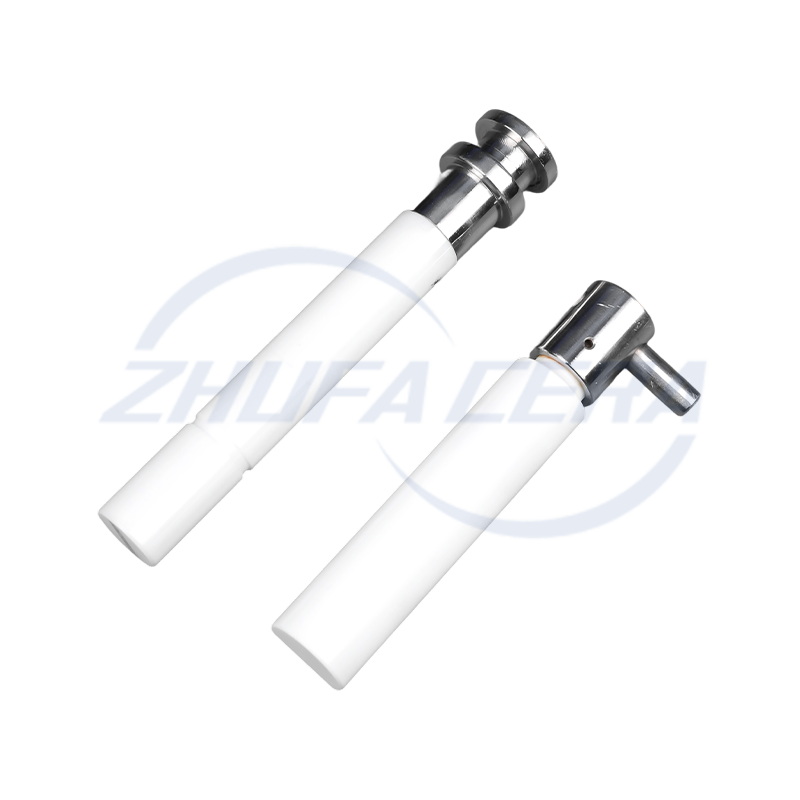
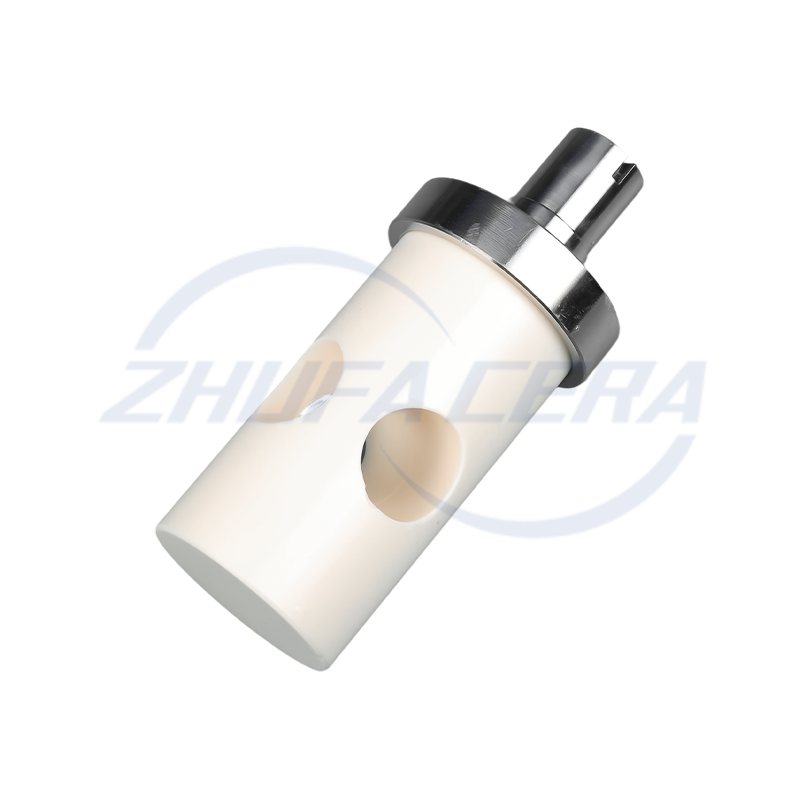
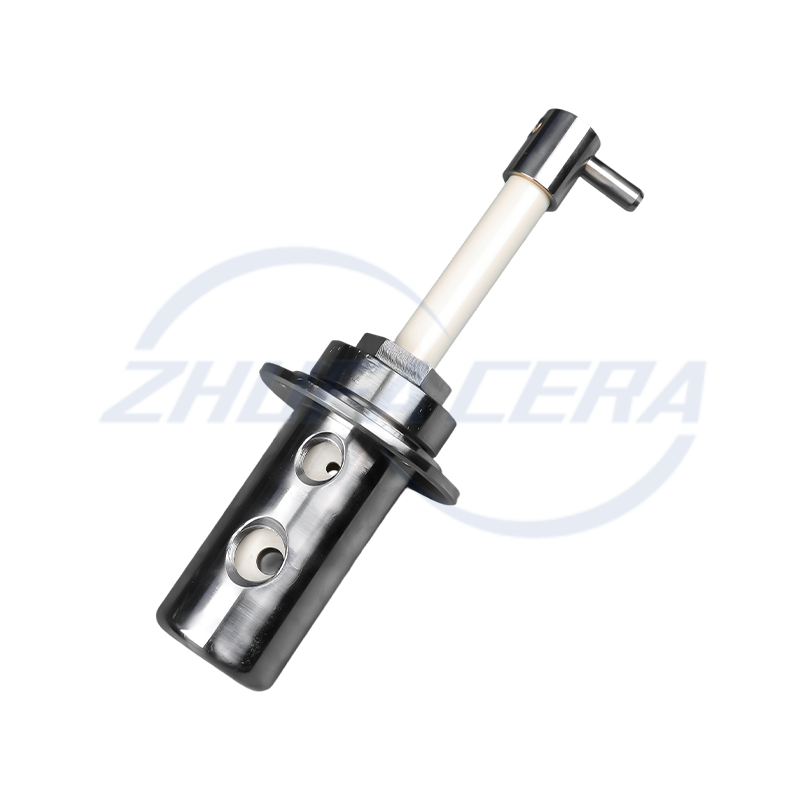
Suppliers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. integrate these key materials into their portfolio, providing customized solutions that span the full spectrum of oxide, nitride, and carbide ceramics to meet diverse industrial needs.
2. Key Manufacturing Processes of New Ceramic Structural Parts
The manufacturing of high-performance ceramic structural parts is a precision-driven sequence, with each step critical to final product quality.
2.1 Powder Preparation: The Foundation of Performance
Powder quality directly determines ceramic performance, as purity, particle size distribution, and morphology influence sintering behavior and final material properties . Advanced preparation methods include chemical precipitation for nanoscale powders and gas-phase synthesis for high-purity formulations, ensuring consistency in subsequent processing stages . Manufacturers prioritize this foundational step—for instance, Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics integrates rigorous raw material processing into its end-to-end production workflow to lay the groundwork for high-performance components.
2.2 Forming: Shaping Precision
Forming transforms ceramic powders into "green bodies" (unfired preforms) and is selected based on component complexity and precision requirements:
Dry Pressing & Cold Isostatic Pressing: Suitable for relatively simple shapes, these methods ensure uniform density; cold isostatic pressing enhances density for high-strength applications .
Injection Molding: Ideal for complex geometries with tight tolerances, enabling mass production of intricate parts .
State-of-the-art facilities like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics’ 30,000㎡ manufacturing base are equipped with all three core forming technologies, supporting both standard and non-standard component production.
2.3 Sintering: Densification & Performance Enhancement
Sintering is the transformative step where green bodies are heated to high temperatures, fusing powder particles into dense, stable ceramic structures . Key parameters include temperature, holding time, and atmospheric control—high-temperature sintering furnaces are essential for achieving the low porosity and high strength required for structural parts . Rapid sintering technologies like microwave sintering are also emerging to shorten cycles while maintaining quality . Strict sintering process control is a hallmark of reliable manufacturers, with Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics leveraging advanced furnaces to ensure consistent densification across batches.
2.4 Precision Finishing: Meeting Tolerance Demands
Post-sintering processing is critical for achieving industrial-grade precision. CNC engraving machines, surface grinders, and honing equipment refine dimensions and surface quality, ensuring compliance with micron-level tolerances . This step is particularly vital for components like electronic sensors and automotive precision parts. Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics complements its forming and sintering capabilities with a full suite of finishing machinery, enabling it to deliver parts that meet stringent accuracy requirements.
3. Quality Control: Safeguarding Reliability
Quality assurance run through the manufacturing lifecycle, addressing both material properties and dimensional accuracy. Key measures include:
In-process inspection of powder uniformity and green body density;
Post-sintering testing of mechanical strength, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance;
Final dimensional verification using precision metrology tools .
Manufacturers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics adhere to strict control standards from equipment configuration to final inspection, ensuring each component’s performance and reliability.
4. Industrial Applications Driven by Manufacturing Advancement
The versatility of new ceramic structural parts stems from their tailored manufacturing, enabling deployment across high-demand sectors:
Automotive & New Energy: Used in engines, braking systems, and fuel cells, ceramic parts leverage wear and high-temperature resistance to enhance vehicle efficiency and safety—supporting the growth of smart and electric vehicles .
Electronics & Semiconductors: High-purity, insulating ceramic components ensure precision in wafer handling and etching equipment, reducing contamination risks .
Photovoltaics: Ceramics withstand high temperatures in wafer cutting and sintering processes, boosting equipment lifespan and production stability .
Petrochemicals: Corrosion-resistant ceramic valves and seals maintain reliability in harsh chemical environments, lowering maintenance costs .
Suppliers with cross-industry expertise, such as Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics, align their manufacturing flexibility—from small-batch proofing to large-scale production—with these sector-specific demands, delivering application-optimized solutions.
5. Future Trends in Manufacturing
The sector is evolving toward three key directions:
Multifunctional Integration: Developing ceramics with combined properties (e.g., thermal conductivity + insulation) to meet complex application needs .
Advanced Forming Technologies: 3D printing and laser sintering are gaining traction for ultra-complex, customized parts .
Sustainable Manufacturing: Adopting energy-efficient sintering and powder recycling to reduce environmental impact .
Forward-looking manufacturers are integrating these trends into their capabilities—Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics, for example, emphasizes agile manufacturing and technical collaboration to adapt to evolving material and process innovations, supporting clients’ competitiveness in advancing industries.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어