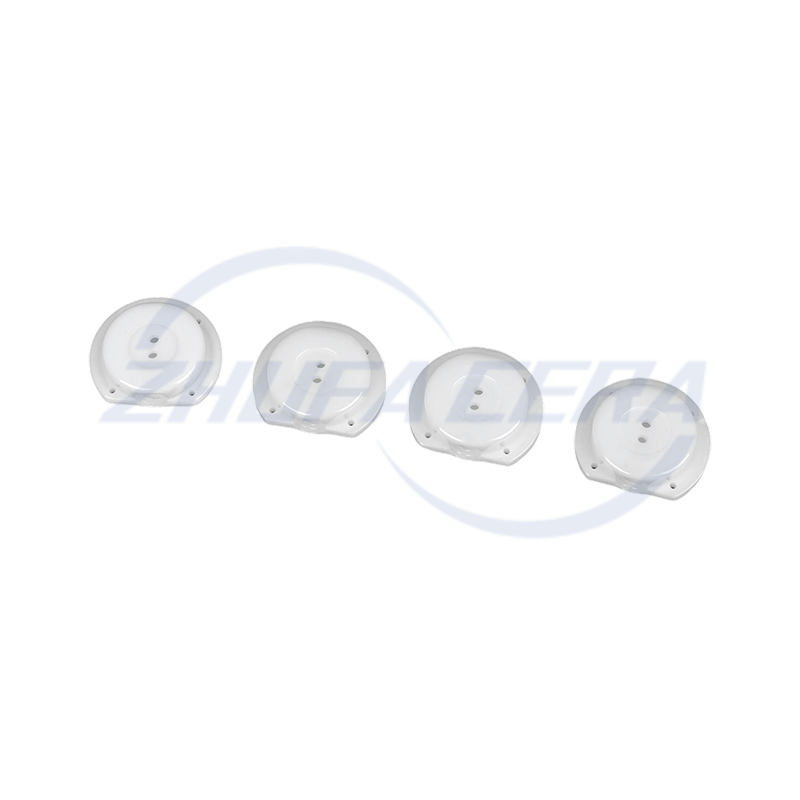
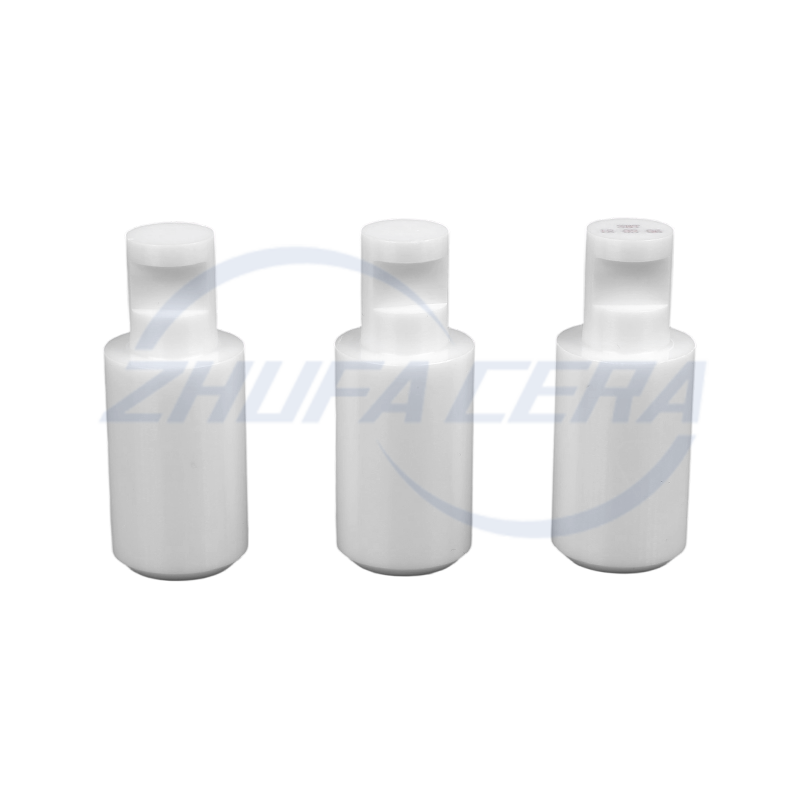
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
What issues should be considered when using ZTA ceramics in practical applications?
2026-02-07
Content
ZTA Ceramics (Zirconia Toughened Alumina) are advanced materials that combine the toughness of zirconia with the hardness of alumina. Widely used in various industrial applications, including cutting tools, bearings, and medical devices, ZTA ceramics are renowned for their superior mechanical properties and wear resistance. However, like any high-performance material, there are specific factors to consider when using ZTA ceramics in real-world applications. Understanding these issues is crucial to maximizing their performance and longevity.
Factors Affecting ZTA Ceramic Performance
The performance of ZTA ceramics can be influenced by several key factors. These include the material's composition, processing methods, and the conditions under which they are used. Below are the critical factors to keep in mind:
- Material Composition: The proportion of zirconia and alumina in the ceramic material plays a significant role in its mechanical properties. The right balance of these components is crucial for optimal toughness and wear resistance.
- Processing Method: The manufacturing process, such as sintering temperature and time, can impact the microstructure of ZTA ceramics. Inconsistent processing can lead to defects or reduced material performance.
- Environmental Conditions: ZTA ceramics are highly durable, but exposure to extreme temperatures or corrosive environments can affect their performance. It's important to ensure that the ceramic material is suited for the specific conditions in which it will be used.
Common Challenges with ZTA Ceramics
While ZTA ceramics are known for their toughness and resistance to wear, there are several challenges associated with their use:
- Cracking and Fracture: ZTA ceramics are tough but can still be prone to cracking under high stress or impact. Proper design and handling are necessary to prevent fractures during use.
- Machining Difficulties: Due to their hardness, ZTA ceramics can be difficult to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques to achieve precise shapes and sizes.
- Thermal Expansion: ZTA ceramics have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion than metals, which can cause issues in applications involving significant temperature fluctuations. The mismatch in expansion rates can lead to stress and potential failure.
Key Considerations in the Use of ZTA Ceramics
When incorporating ZTA ceramics into practical applications, several key considerations should be kept in mind:
- Design Flexibility: ZTA ceramics are versatile, but their brittleness at certain thicknesses can limit their applications. Designers must take this into account to ensure that components are appropriately sized and shaped.
- Maintenance and Care: ZTA ceramics are low-maintenance materials; however, care should be taken to avoid impact damage. Cleaning methods should also avoid harsh abrasives that could compromise the material’s surface.
- Compatibility with Other Materials: In applications where ZTA ceramics are used in combination with other materials, such as metals or plastics, the compatibility between materials must be considered, especially in terms of thermal expansion and mechanical load-bearing capacity.
Performance Comparison: ZTA Ceramics vs. Other Ceramic Materials
In many applications, ZTA ceramics are compared with other types of advanced ceramics, such as traditional alumina or pure zirconia. Below is a comparison highlighting the advantages and limitations of ZTA ceramics:
| Property | ZTA Ceramics | Alumina | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toughness | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Hardness | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Machinability | Moderate | Good | Poor |
| Temperature Stability | High | Moderate | Very High |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the primary benefits of ZTA ceramics over traditional ceramics?
ZTA ceramics offer improved toughness and wear resistance compared to traditional ceramics like alumina. The zirconia content enhances their ability to withstand high-stress environments, making them ideal for applications like cutting tools, medical devices, and industrial bearings.
2. Can ZTA ceramics be used in high-temperature applications?
Yes, ZTA ceramics have excellent temperature stability, making them suitable for high-temperature environments. However, it is important to consider the specific temperature range and thermal expansion properties when using them in such applications.
3. Are ZTA ceramics prone to cracking?
While ZTA ceramics are known for their toughness, they are still susceptible to cracking under extreme impact or stress. Proper handling and design are essential to prevent fractures.
4. How can ZTA ceramics be machined?
Due to their hardness, ZTA ceramics require specialized tools and techniques for machining. Diamond-coated tools are commonly used to achieve precision cuts. Laser machining and abrasive water jet cutting are also effective methods.
5. What industries benefit from ZTA ceramics?
ZTA ceramics are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, electronics, and mining. Their exceptional wear resistance, high strength, and temperature stability make them a valuable material in demanding applications.
Conclusion
ZTA ceramics are an advanced material that combines the best properties of zirconia and alumina, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. However, their successful use depends on understanding the material's limitations and potential challenges. By considering factors like design, processing methods, and environmental conditions, users can maximize the benefits of ZTA ceramics while minimizing potential issues. Proper handling, maintenance, and compatibility with other materials will also help ensure the long-term performance and durability of components made from ZTA ceramics.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어