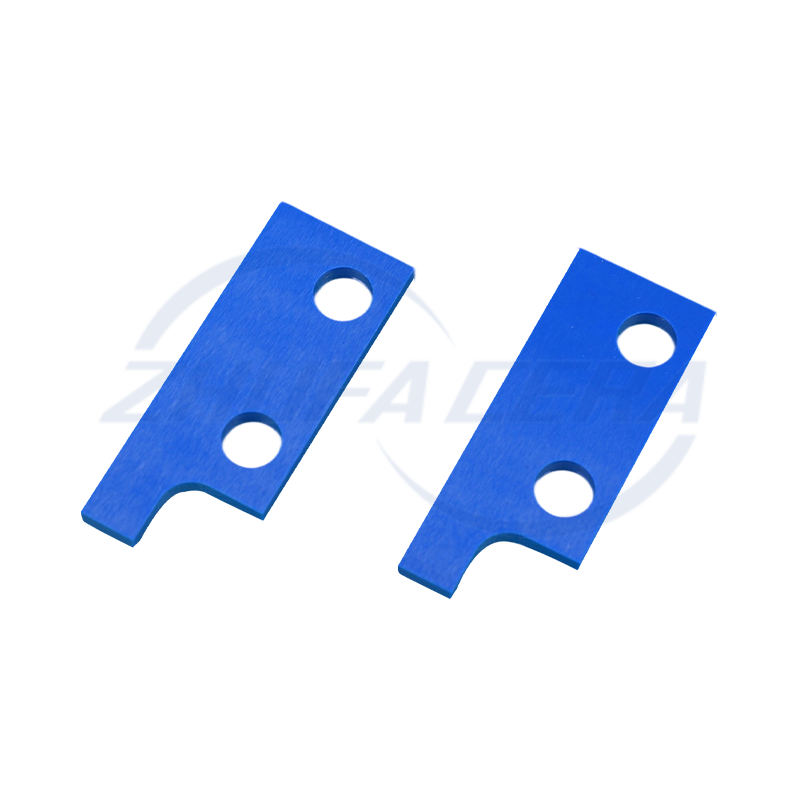
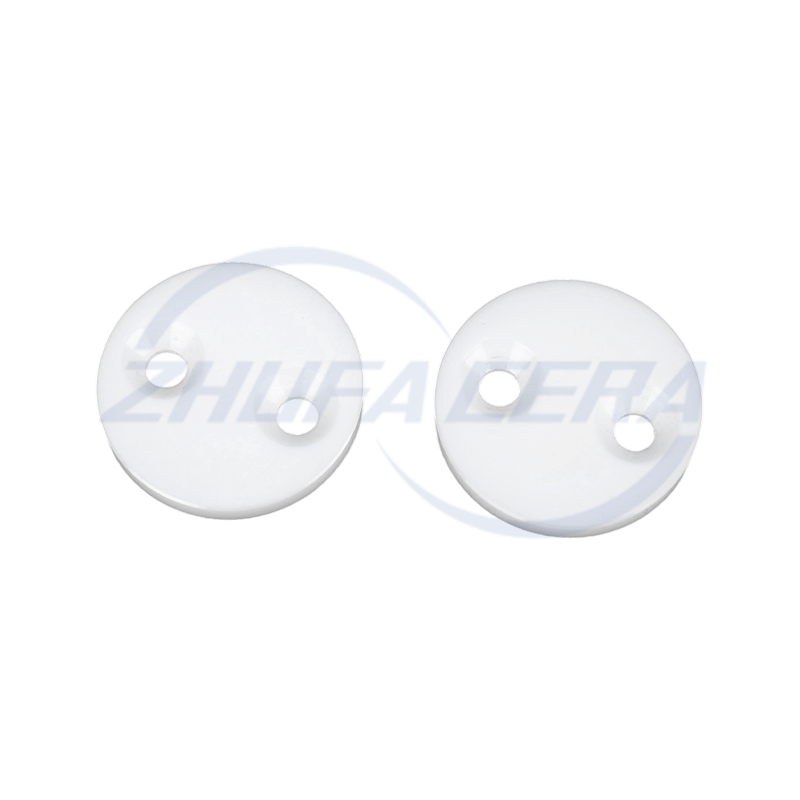
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Is ZTA Ceramics Suitable for High-Load Mechanical Components?
2026-01-31
Content
- What Are ZTA Ceramics?
- Key Material Properties of ZTA Ceramics
- Why High-Load Mechanical Components Demand Advanced Materials
- Advantages of ZTA Ceramics in High-Load Mechanical Applications
- Limitations and Considerations When Using ZTA Ceramics
- Comparison: ZTA Ceramics vs Other Materials
- Typical High-Load Applications of ZTA Ceramics
- Design Guidelines for Using ZTA Ceramics in High-Load Systems
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Are ZTA Ceramics the Right Choice for High-Load Mechanical Components?
As industrial equipment continues to evolve toward higher loads, higher speeds, and harsher operating environments, material selection has become a critical factor influencing performance, safety, and lifecycle cost. Traditional materials such as alloy steel, cast iron, and engineering plastics are increasingly challenged by extreme wear, corrosion, and thermal stress. Against this background, ZTA Ceramics—also known as Zirconia Toughened Alumina Ceramics—have gained growing attention in heavy-duty mechanical applications.
What Are ZTA Ceramics?
Basic Composition and Structure
ZTA Ceramics are composite ceramic materials primarily composed of:
- Alumina (Al2O3) as the main structural phase
- Zirconia (ZrO2) as a toughening agent
By dispersing fine zirconia particles uniformly within the alumina matrix, ZTA Ceramics achieve enhanced fracture resistance without sacrificing hardness. The zirconia phase undergoes stress-induced phase transformation, which helps absorb crack energy and prevent crack propagation.
How ZTA Ceramics Differ from Traditional Alumina
While standard alumina ceramics are known for their high hardness and chemical stability, they are also brittle. ZTA Ceramics address this weakness by significantly improving toughness, making them more suitable for applications involving mechanical shock and sustained high loads.
Key Material Properties of ZTA Ceramics
The suitability of any material for high-load mechanical components depends on a combination of physical, mechanical, and thermal properties. ZTA Ceramics perform exceptionally well across multiple dimensions.
| Property | ZTA Ceramics | Typical Impact on High-Load Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | HV 1500–1800 | Excellent resistance to abrasive wear |
| Fracture Toughness | 6–9 MPa·m1/2 | Reduced risk of catastrophic failure |
| Bending Strength | 600–900 MPa | Handles sustained mechanical stress |
| Compressive Strength | >3000 MPa | Ideal for load-bearing components |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1000°C | Suitable for high-temperature environments |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Performs well in corrosive media |
Why High-Load Mechanical Components Demand Advanced Materials
Common Challenges in High-Load Environments
High-load mechanical components are subjected to a combination of:
- Continuous compressive and shear forces
- Repeated impact or cyclic loading
- Severe abrasion and erosion
- High operating temperatures
- Chemical corrosion or oxidation
Materials used in such environments must maintain dimensional stability and mechanical integrity over long periods. Traditional metals often suffer from wear, deformation, fatigue, and corrosion, leading to frequent maintenance and replacement.
Advantages of ZTA Ceramics in High-Load Mechanical Applications
Outstanding Wear and Abrasion Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of ZTA Ceramics is their superior wear resistance. Under high-load sliding or abrasive conditions, ZTA components experience minimal material loss compared to steel or cast iron.
This makes them particularly suitable for:
- Wear plates
- Liners
- Guide rails
- Valve seats
High Compressive Strength for Load-Bearing Roles
ZTA Ceramics exhibit extremely high compressive strength, allowing them to withstand intense mechanical loads without plastic deformation. Unlike metals, they do not creep under sustained stress at elevated temperatures.
Improved Toughness Compared to Conventional Ceramics
Thanks to zirconia toughening, ZTA Ceramics are far less brittle than traditional alumina. This improvement significantly reduces the likelihood of sudden fracture under high-load or impact conditions.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Attack
In chemically aggressive environments—such as mining slurry systems or chemical processing equipment—ZTA Ceramics outperform metals by resisting acids, alkalis, and solvents without degradation.
Longer Service Life and Lower Maintenance Costs
Although the initial cost of ZTA components may be higher, their extended service life often results in a lower total cost of ownership. Reduced downtime and maintenance translate into significant operational savings.
Limitations and Considerations When Using ZTA Ceramics
Sensitivity to Tensile Stress
Like all ceramics, ZTA Ceramics are stronger in compression than in tension. Designs that expose components to high tensile stress must be carefully engineered to avoid failure.
Manufacturing and Machining Constraints
ZTA Ceramics require specialized manufacturing processes such as:
- Hot pressing
- Isostatic pressing
- Precision sintering
Post-sintering machining is more complex and costly than for metals, requiring diamond tools and precise tolerances.
Higher Initial Material Cost
While ZTA Ceramics offer long-term economic benefits, the upfront cost can be higher than steel or polymer alternatives. Cost-benefit analysis is essential when evaluating their use.
Comparison: ZTA Ceramics vs Other Materials
| Material | Wear Resistance | Load Capacity | Toughness | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZTA Ceramics | Excellent | Very High | High | Excellent |
| Alumina Ceramics | Excellent | High | Low | Excellent |
| Alloy Steel | Moderate | High | Very High | Moderate |
| Engineering Plastics | Low | Low | Moderate | Good |
Typical High-Load Applications of ZTA Ceramics
- Mining and mineral processing liners
- High-pressure valve components
- Bearings and bearing sleeves
- Pump wear parts
- Industrial cutting and forming tools
- Mechanical seals and thrust washers
In these applications, ZTA Ceramics consistently demonstrate superior durability and reliability under heavy mechanical loads.
Design Guidelines for Using ZTA Ceramics in High-Load Systems
- Prioritize compressive load paths in component design
- Avoid sharp corners and stress concentrators
- Use compliant mounting systems where possible
- Pair with compatible materials to reduce impact stress
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can ZTA Ceramics replace steel in all high-load applications?
No. While ZTA Ceramics excel in wear, compression, and corrosion resistance, steel remains superior in applications dominated by tensile or bending loads. Proper material selection depends on load type and operating conditions.
Are ZTA Ceramics suitable for impact loading?
ZTA Ceramics perform better under impact than traditional ceramics, but they are not as impact-tolerant as ductile metals. Moderate impact conditions are acceptable when designs are optimized.
Do ZTA Ceramics require lubrication?
In many applications, ZTA Ceramics can operate with minimal or no lubrication due to their low wear rate and smooth surface finish.
How long do ZTA Ceramic components typically last?
Service life depends on operating conditions, but in abrasive and high-load environments, ZTA components often last several times longer than metal alternatives.
Are ZTA Ceramics environmentally friendly?
Yes. Their long service life reduces waste and maintenance frequency, contributing to more sustainable industrial operations.
Conclusion: Are ZTA Ceramics the Right Choice for High-Load Mechanical Components?
ZTA Ceramics offer a compelling combination of high hardness, excellent wear resistance, enhanced toughness, and exceptional compressive strength. For high-load mechanical components operating in abrasive, corrosive, or high-temperature environments, they represent a technically advanced and economically viable solution.
While they are not a universal replacement for metals, when properly designed and applied, ZTA Ceramics significantly outperform traditional materials in demanding industrial applications. As industries continue to push the limits of performance and efficiency, ZTA Ceramics are poised to play an increasingly important role in next-generation mechanical systems.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어