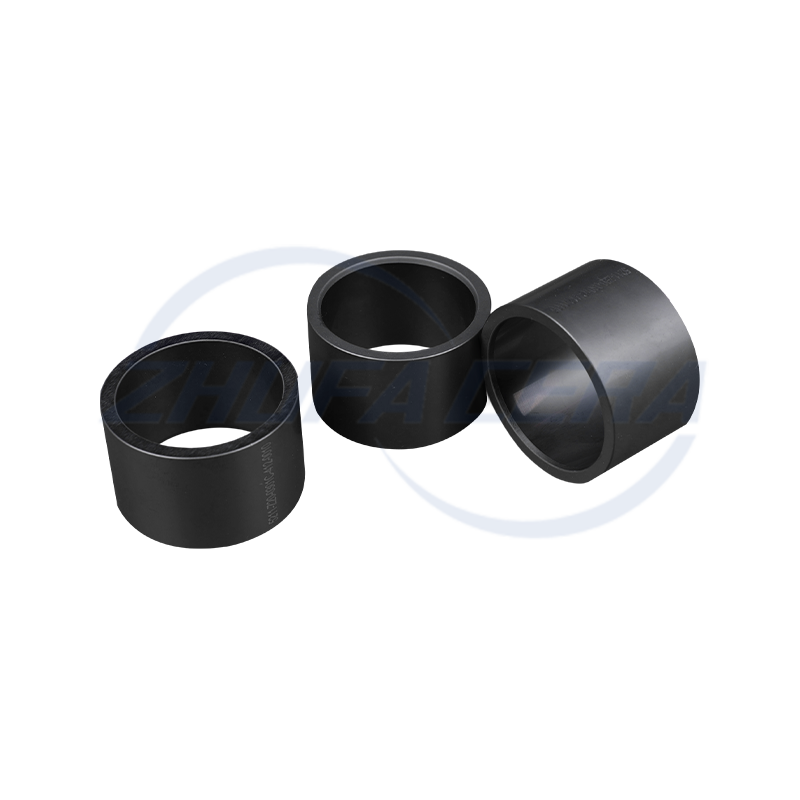
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Does ZTA Ceramics have applications in medical or bioceramics?
2026-01-23
Content
Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA) ceramics have emerged as a significant material in a wide range of applications due to their excellent combination of toughness, hardness, and biocompatibility. ZTA ceramics are particularly noted for their use in the medical and bioceramics fields, where their unique properties meet the stringent demands of the industry.
What is ZTA Ceramics?
ZTA ceramics are composites made by combining zirconia (ZrO2) and alumina (Al2O3). Zirconia provides toughness, while alumina contributes to high wear resistance and strength. This combination results in a ceramic material with superior fracture toughness, mechanical properties, and thermal stability. These attributes make ZTA ceramics particularly useful in applications where traditional materials might fail, such as in demanding medical and biotechnological applications.
Key Properties of ZTA Ceramics
Before delving into their applications, it’s important to understand why ZTA ceramics are favored in the medical and bioceramic fields:
- High Biocompatibility: ZTA ceramics are biologically inert, meaning they don’t interact adversely with human tissue or bodily fluids, making them ideal for implants and prosthetics.
- Superior Strength and Durability: ZTA offers an optimal balance of high strength, wear resistance, and fracture toughness, which is essential for devices that will be subjected to mechanical stress over long periods.
- Thermal Stability: The ceramics retain their integrity even in high-temperature environments, making them suitable for applications in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
- Corrosion Resistance: ZTA ceramics exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for long-term exposure to biological environments such as in the body.
ZTA Ceramics in Medical Applications
1. Dental Implants
Dental implants made from ZTA ceramics have gained immense popularity due to their strength, biocompatibility, and ability to mimic the natural appearance of teeth. ZTA ceramics are used to create dental crowns, bridges, and implants, as they offer exceptional wear resistance and aesthetic appeal. Their high strength ensures they can withstand the forces of biting and chewing, while their biocompatibility reduces the risk of rejection or inflammation.
2. Orthopedic Prosthetics
In orthopedic medicine, ZTA ceramics are used in hip replacements, knee replacements, and other joint prosthetics. The material’s combination of toughness and wear resistance ensures that these implants maintain their integrity over time, even under the stress of heavy usage. ZTA’s low friction and high resistance to abrasion make it an excellent choice for creating prosthetic joints that can function in the body for years.
3. Surgical Tools
ZTA ceramics are increasingly used in the production of surgical tools, such as scalpel blades, knives, and scissors. The hardness and durability of ZTA ceramics ensure that surgical tools maintain sharpness for a longer period compared to conventional steel tools. Additionally, these ceramics’ biocompatibility reduces the risk of infection during surgery.
4. Bone and Cartilage Replacement
ZTA ceramics are being explored for use in bone and cartilage replacement. Their ability to integrate with biological tissue while maintaining their structural integrity makes them an excellent material for creating artificial bones and cartilage. These ceramics are used in combination with other materials to develop customized implants tailored to individual patients' needs.
ZTA Ceramics in Bioceramics
The use of ZTA ceramics extends beyond the medical field and into bioceramics, which includes materials used for tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and more. ZTA ceramics’ properties make them suitable for a variety of applications in the biotechnological field:
1. Tissue Engineering Scaffolds
ZTA ceramics can be used as scaffolds in tissue engineering. These scaffolds provide a structure that encourages the growth of new tissue, which is essential for regenerative medicine. ZTA’s ability to support cellular growth while offering mechanical strength makes it ideal for creating scaffolds for bone and cartilage regeneration.
2. Drug Delivery Systems
ZTA ceramics are being explored for use in drug delivery systems. Their porous structure can be engineered to carry and release pharmaceutical compounds over time. This controlled release mechanism is beneficial for administering drugs at a steady rate, improving patient compliance and treatment effectiveness.
3. Bioactive Coatings for Implants
ZTA ceramics are used as bioactive coatings on implants to promote bone growth and reduce the risk of infection. These coatings help to improve the integration of implants with surrounding tissues, reducing the likelihood of implant failure or rejection.
Comparing ZTA Ceramics with Other Bioceramic Materials
When compared to other bioceramic materials, such as hydroxyapatite (HA) and alumina (Al2O3), ZTA ceramics offer several distinct advantages:
- Stronger and More Durable: ZTA ceramics provide superior fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to other bioceramics. This makes them more durable for long-term use in implants and prosthetics.
- Better Biocompatibility: While materials like hydroxyapatite are effective for bone regeneration, ZTA ceramics offer a broader range of applications due to their superior biocompatibility and ability to perform in harsh biological environments.
- Higher Cost Efficiency: Although ZTA ceramics can be more expensive to produce, their long-lasting properties can make them more cost-effective in the long term, particularly for medical implants that require minimal replacement.
FAQ: Common Questions About ZTA Ceramics
1. Are ZTA ceramics safe for use in the human body?
Yes, ZTA ceramics are biologically inert and do not cause any harmful reactions in the body. This makes them an ideal material for medical implants and prosthetics.
2. How long do ZTA ceramic implants last?
ZTA ceramic implants can last many years, often providing lifelong durability with minimal wear and tear. The material’s high resistance to mechanical stress ensures longevity in various medical applications.
3. Can ZTA ceramics be used in all types of medical implants?
While ZTA ceramics are ideal for many medical applications, their specific use will depend on the requirements of the implant. For example, they may not be suitable for applications requiring extreme flexibility but are excellent for situations where strength and wear resistance are critical.
ZTA ceramics continue to show great promise in both medical and bioceramic fields. Their unique combination of biocompatibility, strength, and durability positions them as an essential material for the future of medical devices, implants, and biotechnological applications. As research and development in this field progress, we can expect even more innovative uses of ZTA ceramics, improving the quality of medical treatments and enhancing the lives of patients worldwide.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어