Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
1. What Are the Core Manufacturing Stages for Precision Ceramic Discs?
The production of high-performance ceramic discs follows a rigorous, multi-stage process that directly determines final product properties like density, strength, and precision. The workflow typically starts with raw material preparation: ceramic powders (such as zirconia, alumina, or silicon carbide) are selected for specific purity and particle size—often sub-micron grades—and blended with binders, dispersants, or plasticizers to form feedstocks like spray-dried powders, aqueous slips, or clay-like doughs . This step is critical, as feedstock quality directly reduces sintering shrinkage and improves green body density.
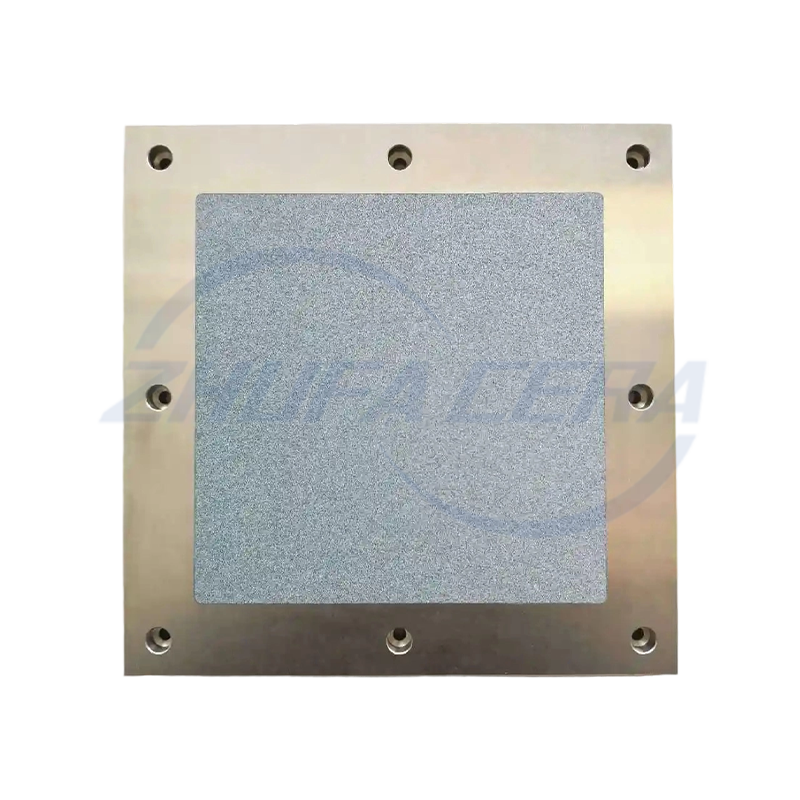
Next comes forming, where feedstocks are shaped into near-net disc forms using techniques matched to material and design requirements. Common methods include dry pressing for simple shapes, cold isostatic pressing for uniform density, and injection molding for complex geometries . Facilities like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. integrate these core forming technologies in their 30,000㎡ manufacturing base to accommodate diverse customization needs .
Sintering follows, using high-temperature furnaces to densify the formed "green" discs, eliminating pores and bonding particles into a rigid ceramic body. For demanding applications like automotive brake discs, advanced processes such as chemical vapor deposition may be added to further increase density—sometimes to 1.95-2.05 g/cm³—enhancing thermal stability . The final stage involves precision finishing: CNC engraving machines, surface grinders, and honing equipment refine dimensions and surface roughness, with zirconia discs often achieving mirror-like finishes of Ra 0.02 . Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. equips its production lines with these finishing tools to meet industrial precision demands .
2. How to Select the Right Ceramic Material for Disc Applications?
Material selection for ceramic discs hinges on aligning key properties with application requirements, as different ceramics offer distinct performance tradeoffs. Alumina (Al₂O₃) is a cost-effective choice with high temperature resistance and electrical insulation, making it ideal for furnace components and electronic substrates . Its Mohs hardness of 9 ensures wear resistance in industrial settings, though its toughness is lower than alternatives .
Zirconia (ZrO₂) excels in high-load, corrosive environments due to its superior toughness (four times that of alumina) and compressive strength, driven by its higher density (6.05 g/cm³ vs. alumina’s 3.7 g/cm³) . Its smooth surface finish also reduces friction, suiting it for valves, pumps, and precision mechanical parts. For extreme thermal conditions—such as automotive brake discs or exhaust systems—silicon carbide (SiC) is preferred for its ability to withstand 1300℃ without thermal softening, often reinforced with carbon fibers for added durability .
Suppliers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. simplify material selection by offering end-to-end support for zirconia, alumina, silicon carbide, and other advanced ceramics, with engineering teams advising on alignment between material properties and application needs like wear resistance in petrochemical seals or insulation in electronics .
3. What Quality Control Measures Ensure Ceramic Disc Reliability?
Reliable ceramic discs depend on multi-stage quality control (QC) that tracks products from raw materials to final inspection. At the feedstock stage, powder purity and particle size are verified to prevent defects in forming and sintering. For mold-based processes, pre-production tooling inspections and ongoing maintenance are mandatory to avoid dimensional deviations .
During production, in-process checks monitor critical parameters: surface roughness, flatness, and contact area ratio are continuously measured to maintain consistency . After sintering, 100% optical inspection (AOI) systems analyze disc surfaces, edges, and dimensions with high precision . For high-stakes applications like automotive sensors or semiconductor equipment, additional testing includes thermal shock resistance and corrosion performance evaluations.
Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. embeds such QC protocols in its workflow, combining strict process controls with advanced inspection equipment to ensure each disc meets performance and reliability standards for industries ranging from new energy vehicles to photovoltaics .
4. How Do Ceramic Discs Meet Industry-Specific Performance Demands?
Ceramic discs are tailored to industry needs through material engineering and precision manufacturing, addressing unique environmental and functional challenges. In automotive applications—such as braking systems and sensors—silicon carbide discs withstand extreme temperatures (up to 1300℃) and reduce noise, while piezo-ceramic discs enable accurate acceleration or knock sensor operation . Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. supplies such discs to enhance vehicle safety and durability, leveraging properties like wear resistance and insulation .
In electronics and semiconductors, high-purity alumina or aluminum nitride discs provide thermal stability and electrical insulation for wafer handling and etching equipment, minimizing contamination risks . For petrochemical pumps and valves, zirconia or silicon carbide discs resist corrosive chemicals and abrasive media, cutting maintenance costs by extending service life .
In photovoltaics, ceramic discs used in wafer cutting and high-temperature sintering processes rely on wear resistance to maintain production efficiency—suppliers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. deliver these components with customized dimensions to fit specific equipment configurations .
5. What Supports Custom Ceramic Disc Production for Low-Volume Needs?
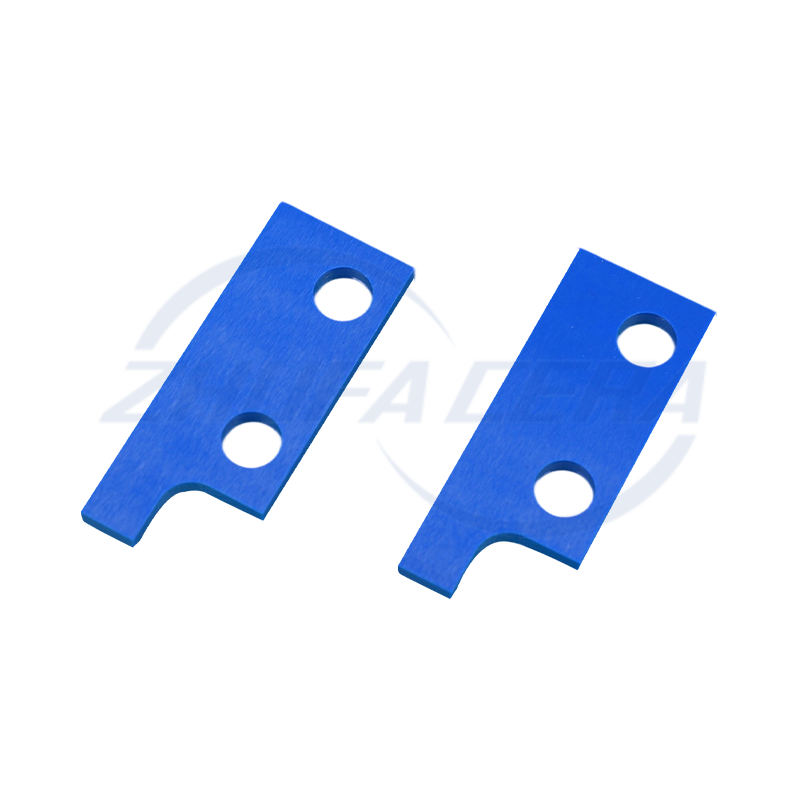
Custom ceramic disc manufacturing for small batches requires flexible production capabilities and direct engineering collaboration. Key enablers include in-house access to multiple forming technologies (e.g., isostatic pressing, injection molding) to accommodate diverse shapes and sizes without sacrificing precision . Rapid prototyping is essential, allowing clients to test designs before scaling, with adjustments guided by engineering expertise.
Suppliers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. specialize in this model, offering end-to-end custom services from prototyping to small-batch production. Their cross-industry experience helps optimize designs for specific applications—whether non-standard semiconductor discs or custom automotive seals—while maintaining lead time consistency . This agility ensures even low-volume orders meet performance, precision, and efficiency requirements.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어