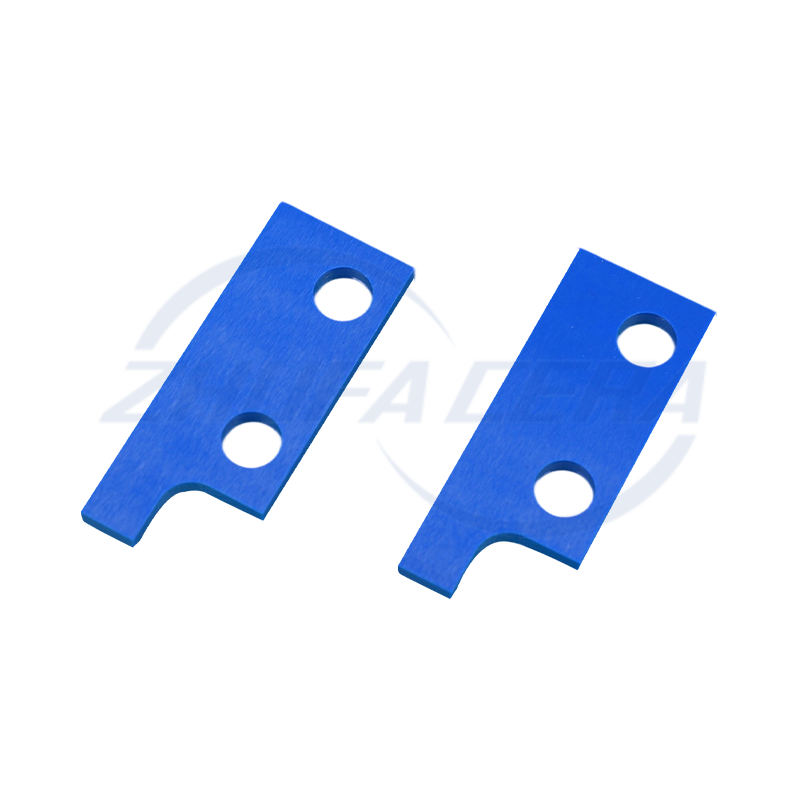
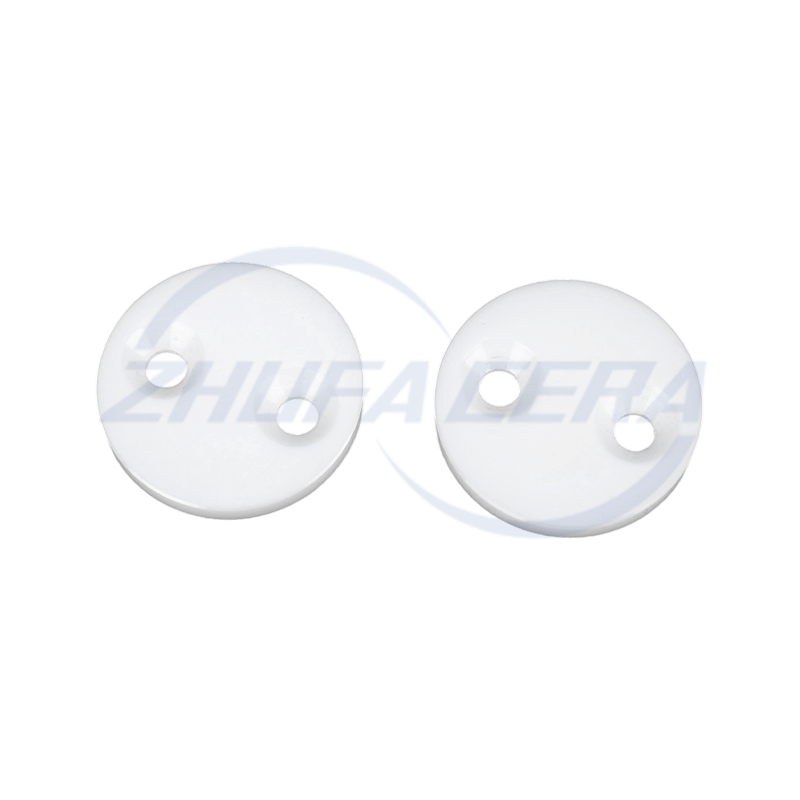
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
How are Precision Ceramics Manufactured?
2025-12-12
Content
Introduction to Precision Ceramics
Precision Ceramics are advanced ceramic materials known for their exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and wear resistance. Widely used in aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and industrial applications, these ceramics require sophisticated manufacturing techniques to achieve precise dimensions and superior material properties.
Key Steps in the Manufacturing Process of Precision Ceramics
1. Raw Material Selection
The process starts with selecting high-purity raw materials, such as alumina, zirconia, silicon nitride, or silicon carbide. The quality of these materials directly affects the final product’s performance, making meticulous selection essential.
2. Powder Preparation and Mixing
The raw materials are ground into fine powders and mixed with additives to improve processability and mechanical properties. Techniques like ball milling or attrition milling ensure uniform particle size distribution, which is critical for achieving high precision.
3. Shaping and Forming
Various shaping techniques are used to form the ceramic parts, including:
- Pressing: Uniaxial or isostatic pressing compacts the powder into a dense shape.
- Injection Molding: Suitable for complex geometries.
- Extrusion: Used for rods, tubes, and other continuous shapes.
- CIP (Cold Isostatic Pressing): Ensures uniform density in intricate components.
4. Sintering
Sintering is a critical step where shaped ceramics are heated to high temperatures below their melting point. This process bonds the particles, reduces porosity, and enhances mechanical strength. Techniques like hot pressing or hot isostatic pressing are often used for Precision Ceramics to achieve superior density and dimensional accuracy.
5. Machining and Finishing
Due to the hardness of Precision Ceramics, conventional machining is challenging. Advanced methods like diamond grinding, laser machining, and ultrasonic machining are employed to achieve precise dimensions and tight tolerances. Surface finishing may also include polishing to meet optical or functional requirements.
6. Quality Control and Testing
Each component undergoes rigorous quality inspection, including dimensional checks, mechanical testing, and microstructural analysis. Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic inspection ensure the integrity of critical parts.
Comparing Precision Ceramics with Conventional Ceramics
| Feature | Precision Ceramics | Conventional Ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | High tolerance (micron-level) | Moderate tolerance |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior, engineered for stress | Moderate, brittle |
| Applications | Electronics, aerospace, medical, precision tools | Construction, cookware, simple components |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why are precision ceramics more expensive than conventional ceramics?
The cost is higher due to the use of high-purity raw materials, advanced manufacturing techniques, and extensive quality control to achieve tight tolerances and superior material properties.
Q2: Can precision ceramics withstand extreme temperatures?
Yes, depending on the material type. For example, zirconia and silicon nitride maintain mechanical strength and dimensional stability at temperatures above 1,000°C.
Q3: Are precision ceramics suitable for medical applications?
Absolutely. Their biocompatibility, wear resistance, and chemical stability make them ideal for implants, surgical instruments, and dental applications.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of Precision Ceramics is a complex, multi-step process that demands high-quality materials, advanced shaping and sintering techniques, and precise machining. These processes ensure that precision ceramic components meet the exacting standards required in high-performance and specialized applications.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어