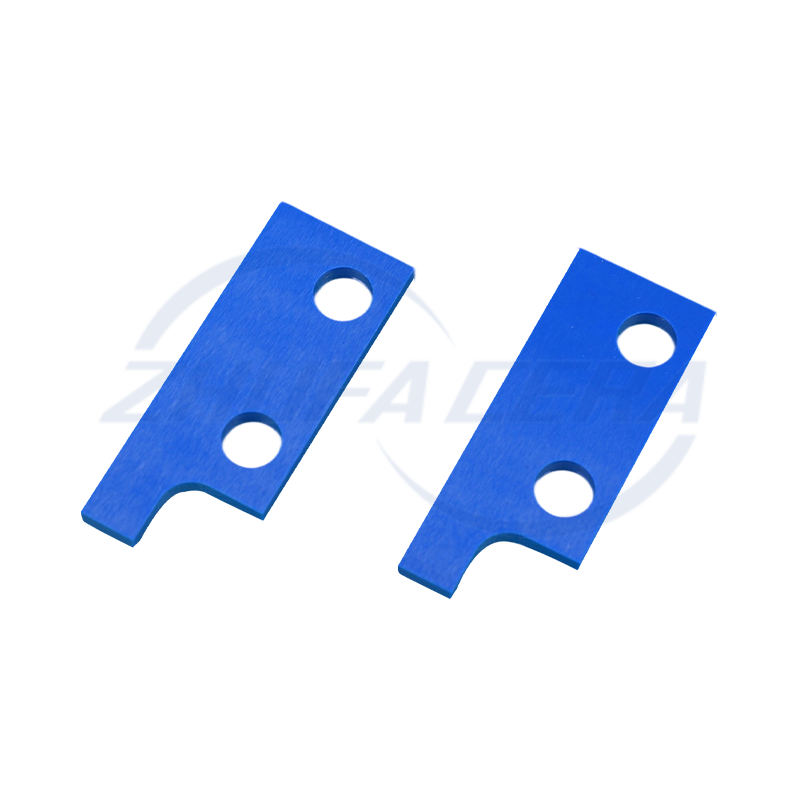
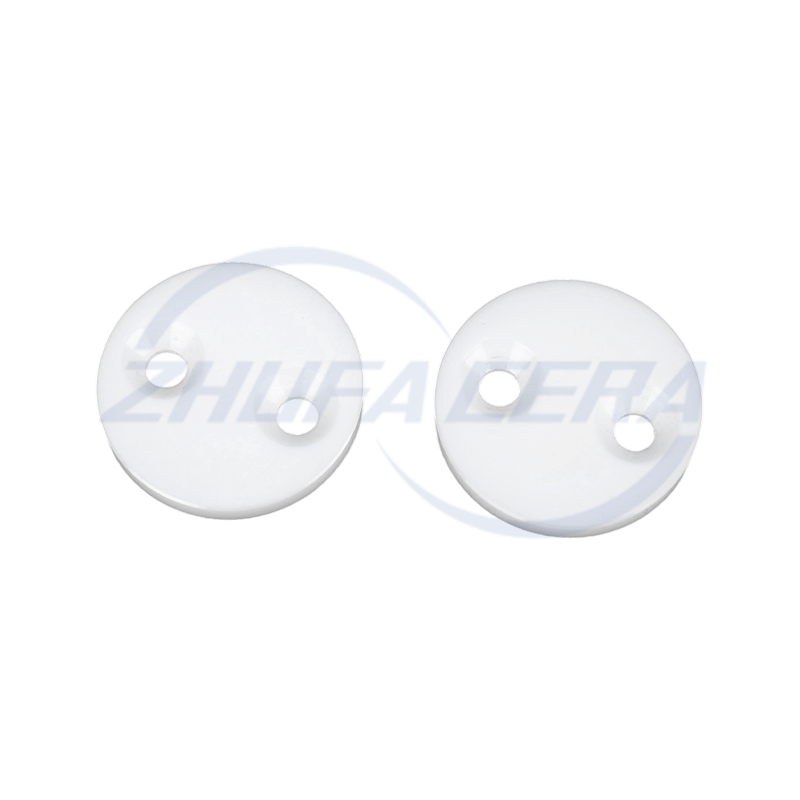
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
What are Precision Ceramics?
2025-12-05
Content
- Understanding Precision Ceramics
- Types of Precision Ceramics
- Manufacturing Processes of Precision Ceramics
- Applications of Precision Ceramics
- Advantages of Precision Ceramics
- Challenges in Precision Ceramics
- Future Trends in Precision Ceramics
- FAQ about Precision Ceramics
- Q1: What is the difference between traditional ceramics and precision ceramics?
- Q2: Can precision ceramics be used in high-temperature environments?
- Q3: Are precision ceramics suitable for medical applications?
- Q4: How are precision ceramics machined?
- Q5: Why are precision ceramics preferred in electronics?
- Conclusion
Precision Ceramics are advanced ceramic materials engineered with high accuracy and specific properties to meet demanding industrial applications. Unlike conventional ceramics, which are primarily used for aesthetic or structural purposes, precision ceramics combine mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance to perform in extreme environments.
Understanding Precision Ceramics
Precision Ceramics, also known as advanced ceramics, are materials designed at the microstructural level to deliver consistent and predictable performance. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides, nitrides, or composites, and are manufactured with techniques that allow tight dimensional tolerances and complex shapes.
Key Properties of Precision Ceramics
- High Hardness: Capable of resisting wear and abrasion, making them suitable for cutting tools and industrial machinery components.
- Thermal Stability: Can withstand extremely high temperatures without deforming or losing performance.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and chemical reactions, making them ideal for harsh chemical environments.
- Electrical Insulation: Excellent dielectric properties for use in electronic and electrical applications.
- Low Thermal Expansion: Maintains dimensional stability under thermal cycling, crucial for precision instruments.
Types of Precision Ceramics
Oxide Ceramics
Oxide ceramics, such as alumina (Al₂O₃) and zirconia (ZrO₂), are widely used due to their excellent electrical insulation, high hardness, and chemical stability. Alumina is common in cutting tools and wear-resistant parts, while zirconia is known for its toughness and is often used in biomedical implants and structural applications.
Non-Oxide Ceramics
Non-oxide ceramics include silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), known for extreme hardness, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. They are ideal for high-temperature components, engine parts, and aerospace applications.
Composite Ceramics
Composite precision ceramics combine multiple materials to enhance specific properties such as toughness, thermal shock resistance, or conductivity. Examples include alumina-titanium carbide composites used in cutting tools and electronic substrates.
Manufacturing Processes of Precision Ceramics
Powder Processing
High-purity ceramic powders are carefully selected and processed to achieve uniform particle size. Techniques such as ball milling, spray drying, and granulation ensure consistency for precise shaping.
Forming Techniques
- Injection Molding: Used for complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy.
- Isostatic Pressing: Provides uniform density for high-performance ceramics.
- Slip Casting: Suitable for intricate components with smooth surfaces.
Sintering and Hot Pressing
Sintering involves heating the formed ceramic at high temperatures to fuse particles together. Hot pressing applies pressure during sintering to enhance density and mechanical strength, which is crucial for precision applications.
Applications of Precision Ceramics
Electronics and Electrical Components
Precision Ceramics are used as insulators, substrates for electronic circuits, and components in sensors due to their dielectric properties and thermal stability.
Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive and aerospace industries, they are applied in engine components, brake systems, and high-temperature insulation, thanks to their lightweight, strength, and heat resistance.
Medical Devices
Zirconia and alumina ceramics are widely used in prosthetics, dental implants, and surgical instruments for their biocompatibility and wear resistance.
Industrial Machinery
Used in cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, bearings, and pumps, precision ceramics increase efficiency and longevity in harsh industrial conditions.
Advantages of Precision Ceramics
- Durability: Longer service life due to resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal degradation.
- Lightweight: High strength-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for aerospace and transportation.
- Precision Performance: Maintains tight tolerances in extreme environments, critical for advanced machinery.
- Environmental Resistance: Can function in chemically aggressive and high-temperature conditions without failure.
Challenges in Precision Ceramics
Despite their advantages, precision ceramics face challenges including brittleness, higher production costs, and complex machining requirements. Advanced manufacturing techniques and material composites are continuously being developed to overcome these limitations.
Future Trends in Precision Ceramics
Innovation in precision ceramics focuses on enhanced toughness, functional composites, and integration with additive manufacturing technologies. Nanostructured ceramics and 3D-printed components are emerging trends that expand their applications in electronics, medical devices, and high-performance machinery.
FAQ about Precision Ceramics
Q1: What is the difference between traditional ceramics and precision ceramics?
Traditional ceramics are used for general structural or aesthetic purposes, whereas precision ceramics are engineered for specific mechanical, thermal, or chemical performance with tight tolerances.
Q2: Can precision ceramics be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, many precision ceramics, such as silicon carbide and alumina, maintain their properties under extreme temperatures and thermal cycling.
Q3: Are precision ceramics suitable for medical applications?
Absolutely. Zirconia and alumina ceramics are biocompatible and used in implants, surgical instruments, and dental applications.
Q4: How are precision ceramics machined?
They require specialized techniques such as diamond grinding, laser machining, and ultrasonic milling due to their hardness and brittleness.
Q5: Why are precision ceramics preferred in electronics?
Their excellent dielectric properties, thermal stability, and mechanical strength make them ideal for electronic substrates, insulators, and sensors.
Conclusion
Precision Ceramics are indispensable materials in modern industries, offering unparalleled performance in wear resistance, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. With advancements in manufacturing and composite technologies, their applications continue to expand, driving innovation across electronics, aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors. Investing in precision ceramics ensures durability, precision, and efficiency in demanding environments.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어