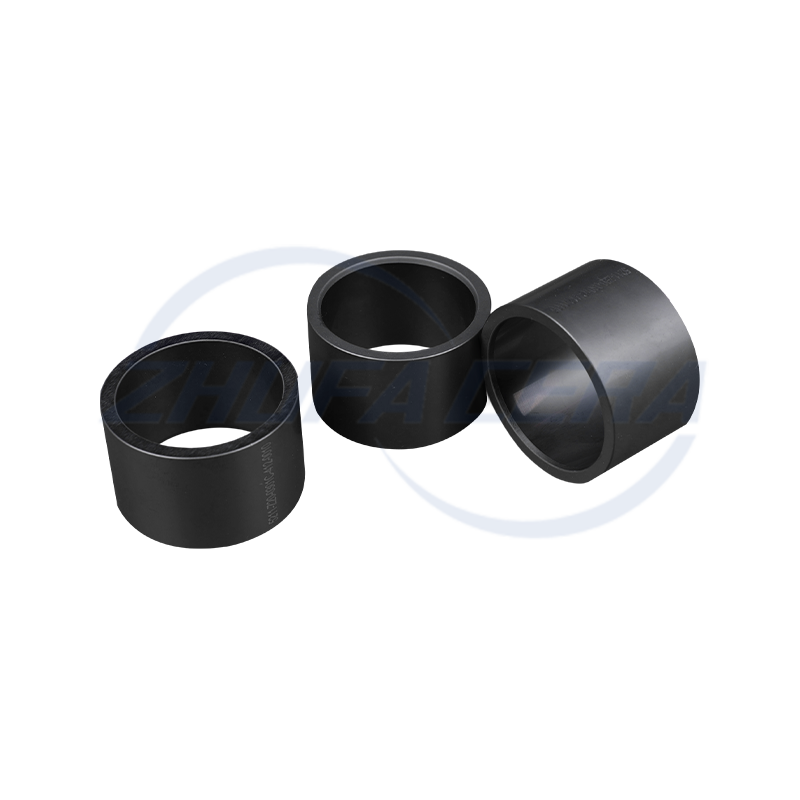
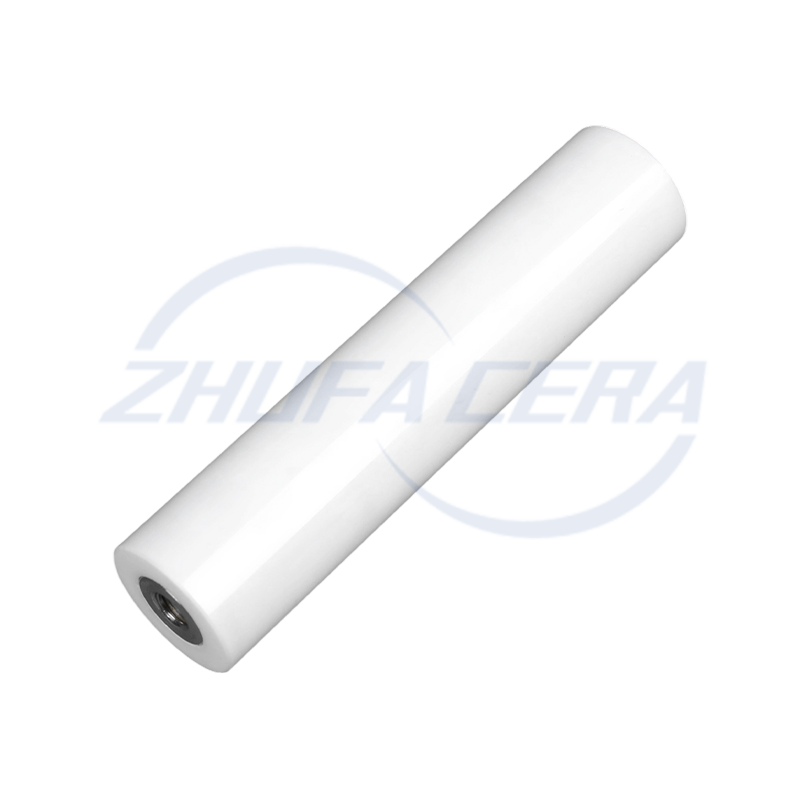
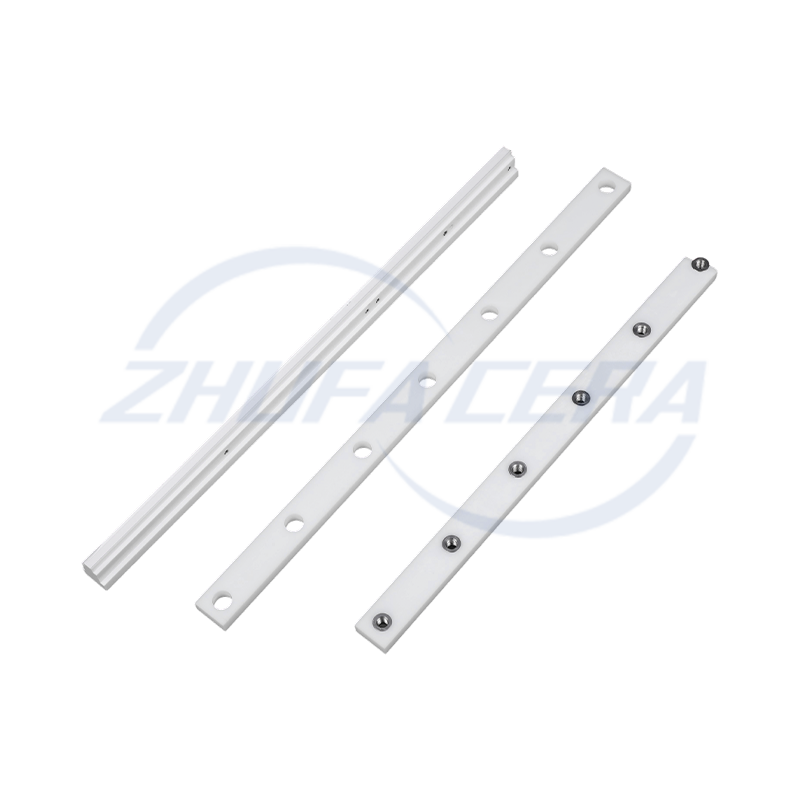
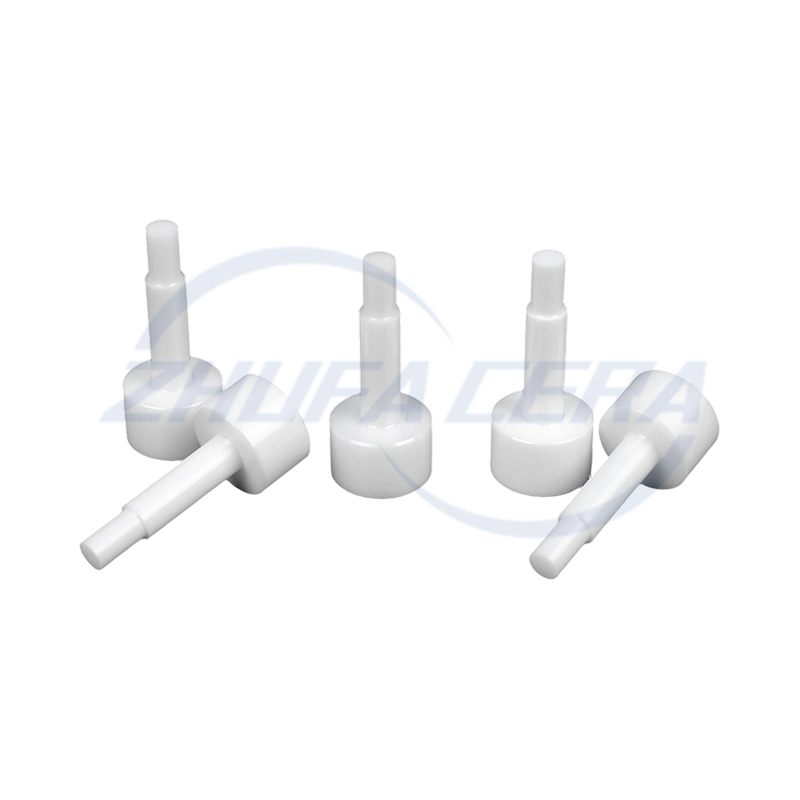
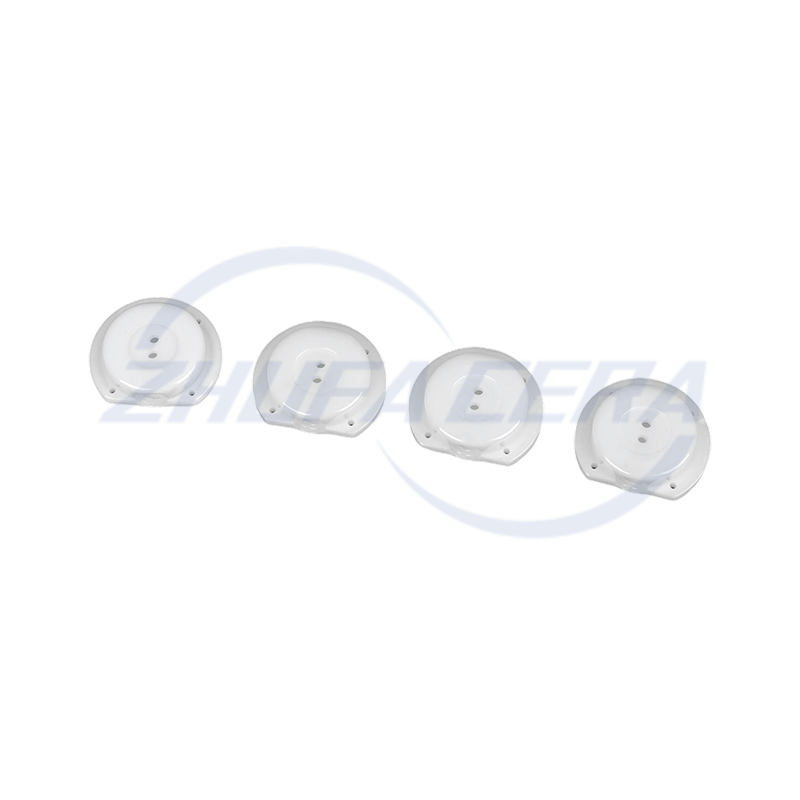
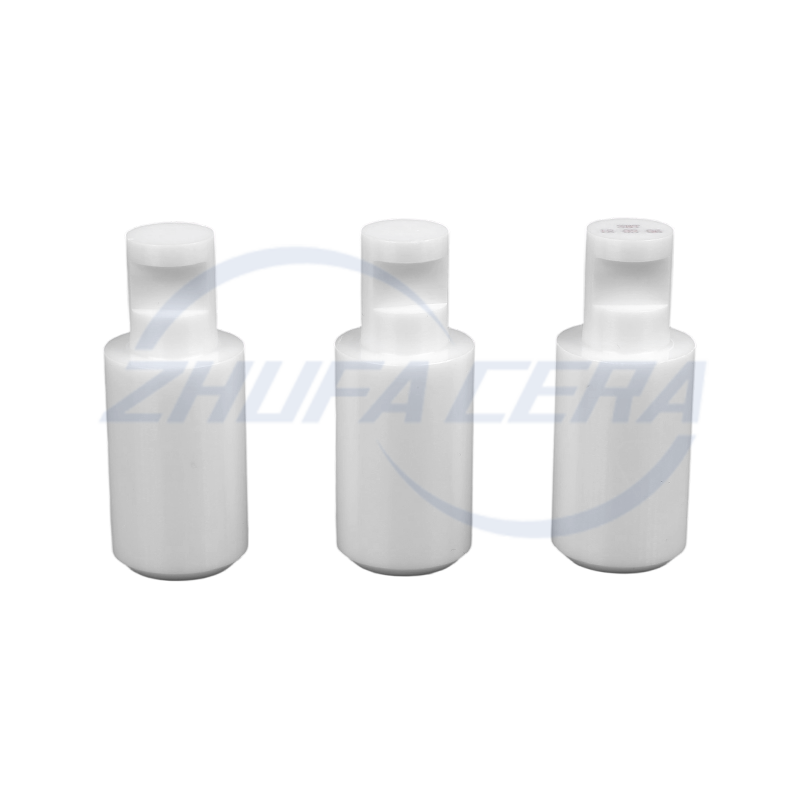
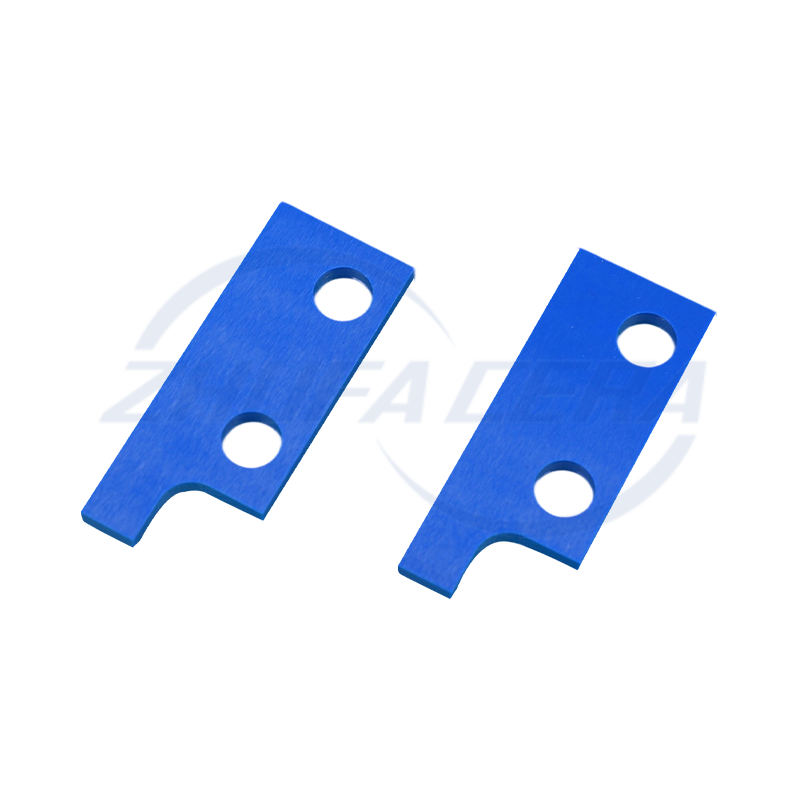
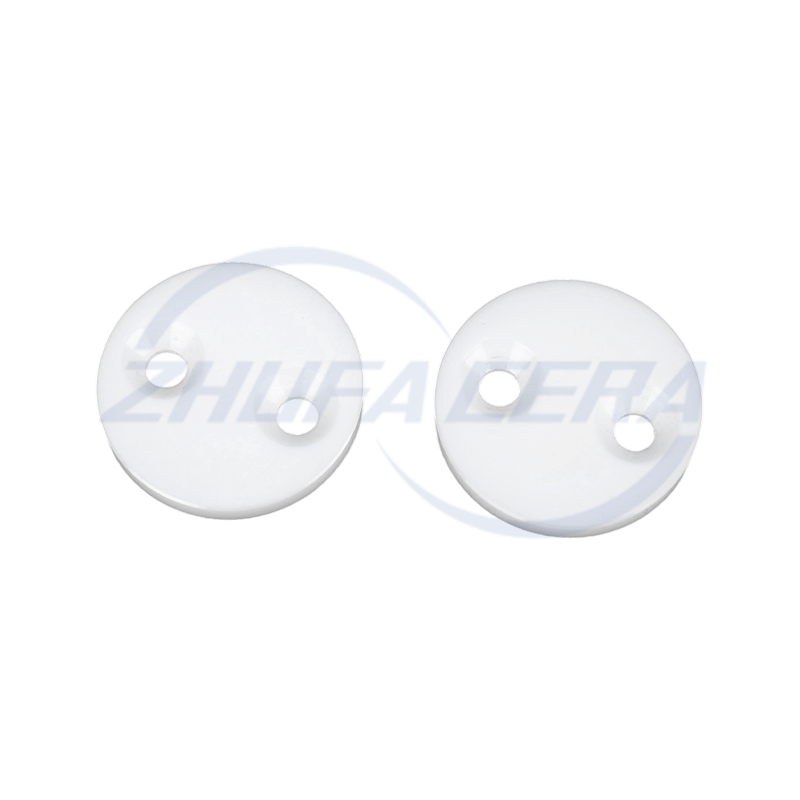
Black silicon carbide ceramic ring is a high-performance engineered ceramic assembly made of high-purity silicon carbide by precision molding and high temperature sintering. Its quadrangular crystal s...
See Details Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
What materials are commonly used in Precision Ceramics?
2025-12-19
Content
Precision Ceramics have become essential in modern industries due to their exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. These materials are widely used in aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and automotive applications where high precision, durability, and reliability are required.
1. Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃)
Alumina is one of the most common materials used in Precision Ceramics. It offers high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and strong thermal stability. Its electrical insulating properties also make it suitable for electronic components.
- High mechanical strength
- Wear and corrosion resistance
- Good electrical insulation
2. Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂)
Zirconia is valued for its toughness, fracture resistance, and high temperature stability. It is often used in medical implants, cutting tools, and high-performance industrial components.
- High fracture toughness compared to other ceramics
- Resistance to wear and thermal shock
- Biocompatibility for medical applications
3. Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Silicon Nitride is known for its superior strength and thermal shock resistance. This material is widely applied in aerospace engines, bearings, and precision machinery components.
- High strength at elevated temperatures
- Excellent thermal shock and chemical resistance
- Low friction coefficient suitable for moving parts
4. Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is highly prized for its extreme hardness and thermal conductivity. It is often used in high-temperature and high-wear environments such as automotive brakes, cutting tools, and industrial machinery.
- Exceptional hardness and wear resistance
- High thermal conductivity
- Resistant to oxidation and chemical attack
5. Boron Carbide (B₄C)
Boron Carbide is a lightweight and extremely hard ceramic material, commonly used in ballistic armor, nuclear applications, and abrasive materials.
- Ultra-high hardness
- Low density for lightweight applications
- Excellent chemical stability
Comparing Precision Ceramic Materials
Each material in Precision Ceramics has unique properties suitable for different applications:
| Material | Key Feature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High wear resistance | Electronics, insulators, substrates |
| Zirconia | High fracture toughness | Medical implants, cutting tools |
| Silicon Nitride | Thermal shock resistance | Aerospace, bearings, engine components |
| Silicon Carbide | Extreme hardness | Industrial machinery, automotive brakes |
| Boron Carbide | Ultra-hard and lightweight | Armor, abrasives, nuclear applications |
Frequently Asked Questions About Precision Ceramics
Q1: What makes a ceramic “precision” ceramic?
Precision Ceramics are manufactured with tight dimensional tolerances and superior material consistency to ensure reliability in critical applications.
Q2: Are Precision Ceramics brittle?
While traditional ceramics are brittle, modern Precision Ceramics such as zirconia and silicon nitride offer improved toughness and fracture resistance.
Q3: How are Precision Ceramics different from conventional ceramics?
Precision Ceramics are designed for high-performance applications, offering better mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance than conventional ceramics used in everyday products.
Q4: Which industries benefit most from Precision Ceramics?
Industries such as aerospace, electronics, medical devices, automotive, and defense rely heavily on Precision Ceramics for critical components that demand durability, accuracy, and performance under extreme conditions.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어