Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Zirconia Ceramics: Manufacturing Insights into Advanced Ceramic Materials
1. Core Properties of Zirconia Ceramics: The "Ceramic Steel" Foundation
Zirconia ceramics stand out as a flagship material in the advanced ceramics sector, earning the title of "ceramic steel" due to their unique combination of strength and toughness that transcends traditional brittle ceramic limitations . At room temperature, they exhibit the highest strength and fracture toughness among all advanced ceramic materials, with bending strength reaching 1200-1400 MPa—surpassing alumina ceramics and approaching some alloy steels . This performance stems from their phase transformation mechanism: pure zirconia exists in monoclinic, tetragonal, and cubic crystal phases at different temperatures, and adding stabilizers like yttria or ceria controls these structural changes to achieve enhanced toughness .
Complementing this mechanical resilience are exceptional functional properties: a melting point of 2700°C enabling long-term use at up to 2400°C, surface hardness of Hv 1200-1400 (15 times more wear-resistant than traditional metals), strong chemical inertness against acids and alkalis, and high electrical insulation with resistivity exceeding 10¹⁴ Ω·cm . These characteristics make zirconia ceramics indispensable across high-demand industrial fields.
2. Key Manufacturing Processes: Precision from Powder to Component
The manufacturing of zirconia ceramics is a highly controlled sequence spanning powder preparation, forming, sintering, and precision finishing—each step critical to final performance.
Powder Preparation: The Starting Point of Quality
High-performance zirconia ceramics require ultra-pure, uniformly dispersed powders with narrow particle size distribution . Common synthesis methods include co-precipitation, hydrothermal synthesis, and sol-gel processes, which produce powders that directly influence sintered density and mechanical strength. Industry standards typically demand powder purity above 99.9% to avoid impurity-induced performance degradation . Manufacturers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. integrate raw material processing into their end-to-end production workflow, laying the groundwork for consistent component quality .
Forming: Shaping for Diverse Requirements
Forming processes are selected based on component geometry and production volume:
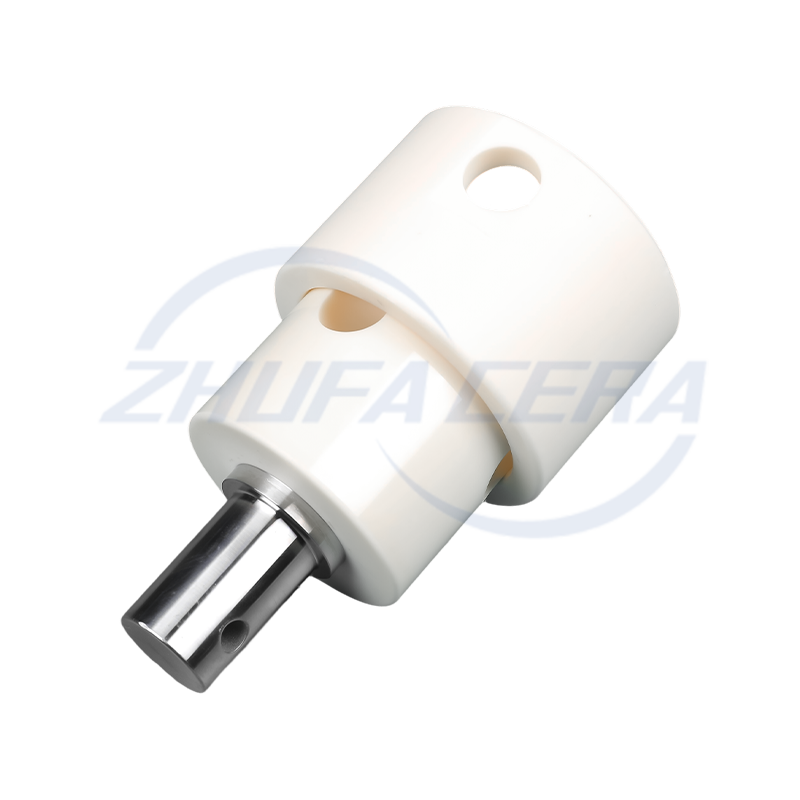
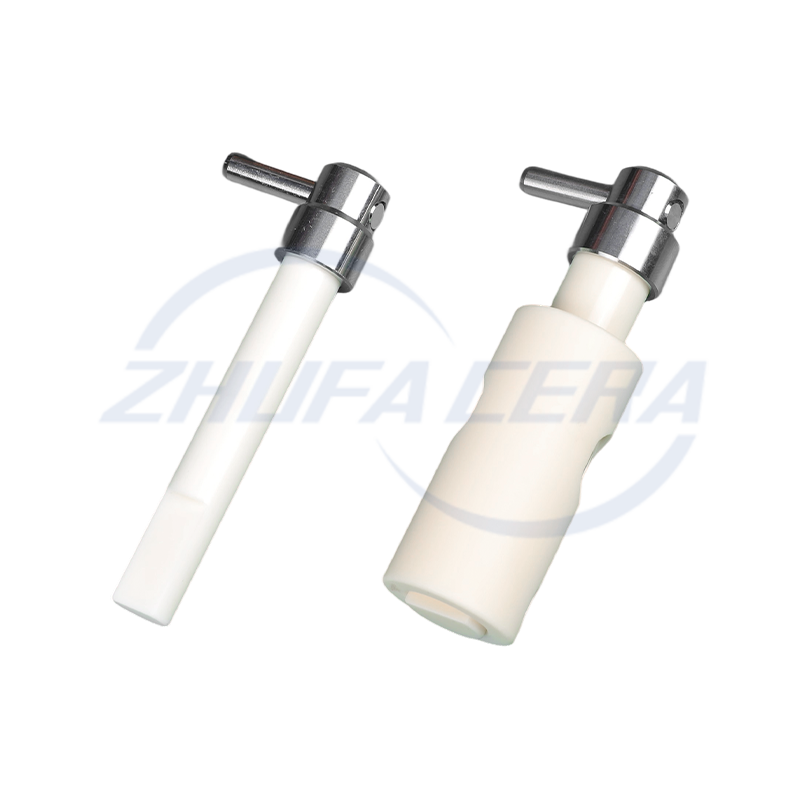
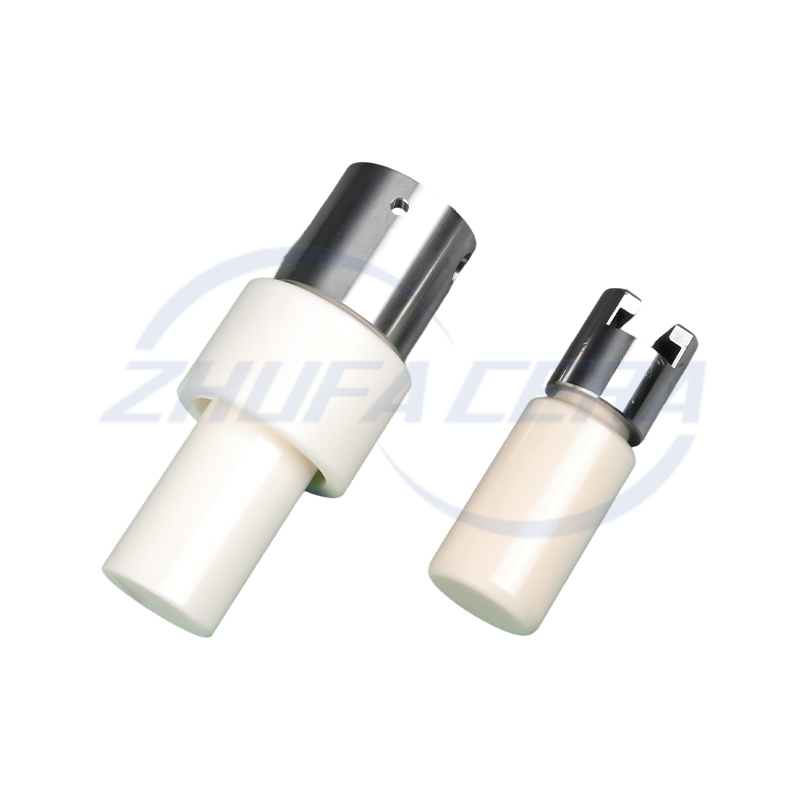
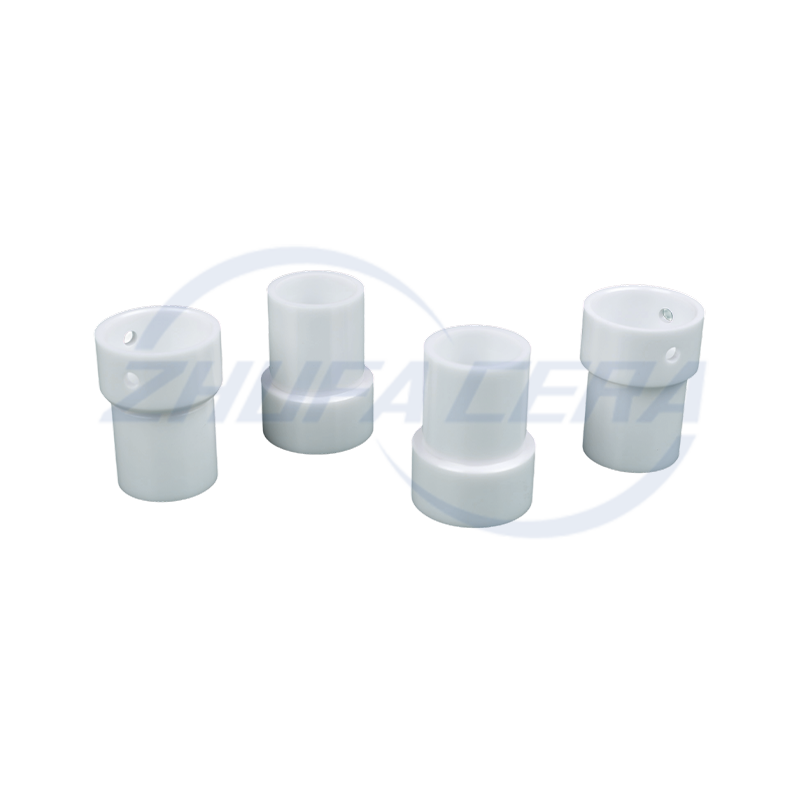
Dry Pressing & Cold Isostatic Pressing: Ideal for relatively simple shapes, these methods ensure uniform density. Cold isostatic pressing enhances green body consistency, a technique employed by facilities equipped with advanced pressing equipment .
Injection Molding: Suited for complex, high-precision parts and large-scale production, it delivers exceptional dimensional accuracy despite requiring specialized tooling .
Laser Cutting: Used for thin substrates (typically ≤1mm thickness), widely applied in electronic components manufacturing .
Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. has built its 30,000㎡ manufacturing base with a full suite of forming equipment—including dry pressing, cold isostatic pressing, and injection molding systems—to accommodate both standard and custom requirements .
Sintering: Achieving Densification and Performance
Sintering transforms green bodies into dense ceramic components, with temperature control being paramount. Most manufacturers utilize high-temperature sintering furnaces for pressureless sintering, the dominant method in the industry . Advanced techniques like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) or spark plasma sintering (SPS) can further improve density and reduce porosity, critical for applications in harsh environments . Strict sintering process control ensures the final product maintains thermal stability and corrosion resistance.
Precision Finishing: Meeting Micron-Level Tolerances
Post-sintering processing is essential for achieving industrial precision requirements. CNC engraving machines, surface grinders, and honing machines are employed to refine dimensions and surface quality, with leading manufacturers achieving tolerances of ±0.01mm . Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. equips its production base with such precision machining tools, supporting non-standard processing and small-batch proofing for diverse industrial needs .
3. Industrial Applications: Driving Innovation Across Sectors
Zirconia ceramics' versatility enables their adoption in strategic emerging industries, aligning with the global advanced ceramics market's shift toward high-value applications .
Automotive & New Energy
In automotive systems—including engines, sensors, fuel cells, and braking systems—zirconia ceramics enhance performance and durability through their wear resistance, high-temperature stability, and insulation . They play a key role in advancing new energy and smart vehicles, where reliability under extreme conditions is critical .
Semiconductor & Electronics
High-purity zirconia components are used in wafer handling, etching, and deposition equipment, ensuring process accuracy while reducing contamination risks . Their non-magnetic properties and thermal stability make them ideal for semiconductor manufacturing, supporting the industry's localization drive .
Petrochemical & Photovoltaics
In petrochemical pumps, valves, and reactors, zirconia's corrosion and wear resistance reduces maintenance costs and extends equipment life . In photovoltaic manufacturing, it withstands the high temperatures of wafer sintering processes, boosting production efficiency .
Medical & Beyond
Biocompatible zirconia variants are widely used in dental crowns and orthopedic implants, meeting ISO 10993 standards for human safety . This medical application segment represents one of the fastest-growing areas for advanced ceramics .







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어