Email: zf@zfcera.com
Email: zf@zfcera.com
 Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
Telephone: +86-188 8878 5188
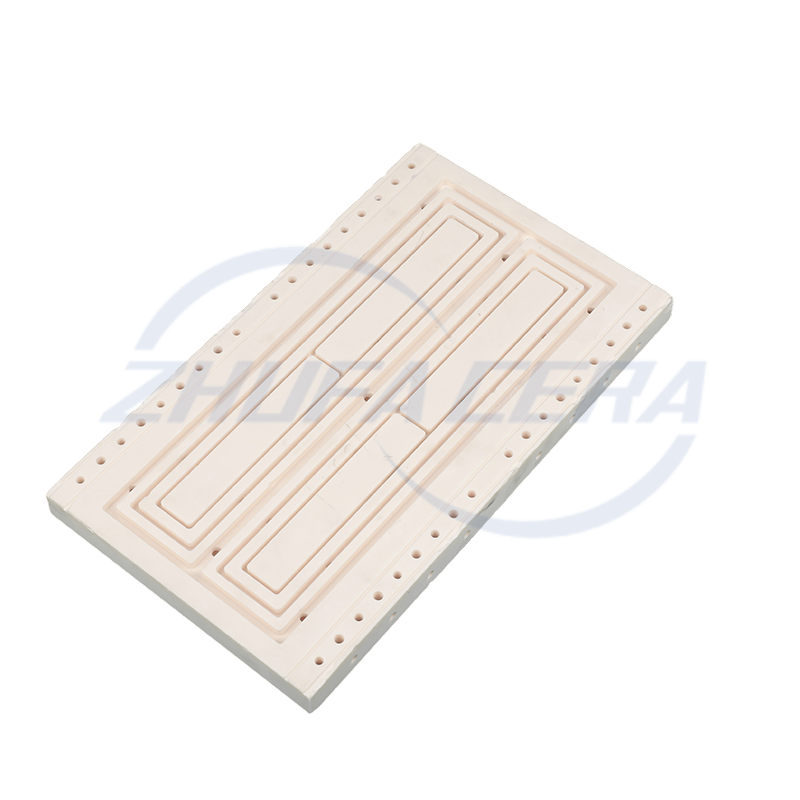
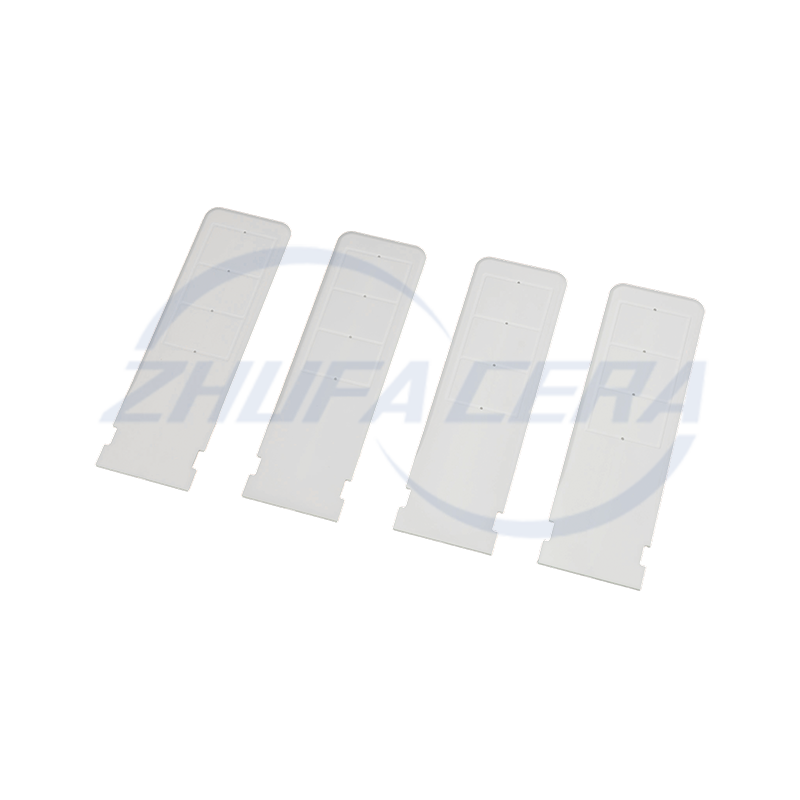
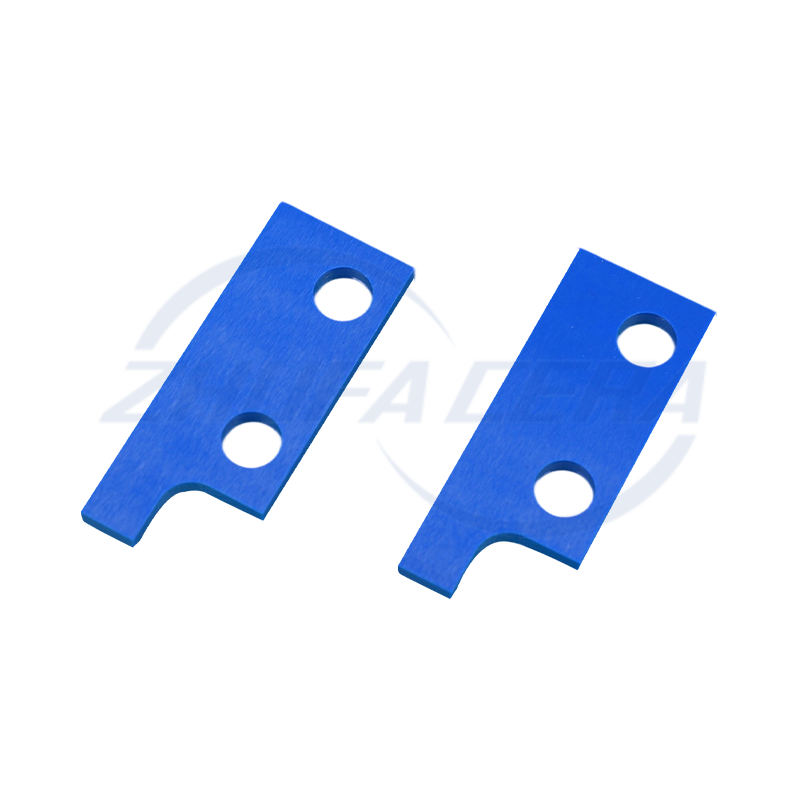
Ceramic Plate: Practical Manufacturing Insights into New Ceramic Materials
What New Ceramic Materials Are Suitable for Industrial Ceramic Plates, and How to Select Them?
The performance of industrial ceramic plates is fundamentally determined by their base materials, with new ceramic materials each offering unique properties tailored to specific application scenarios. Selecting the right material requires aligning key characteristics—such as hardness, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and toughness—with operational demands.
Alumina ceramics are the most versatile option, valued for their balanced performance: high hardness (Mohs hardness 9), excellent insulation, and cost-effectiveness. With purity ranging from 85% to 99.7%, they cater to diverse needs—lower purity grades for general wear-resistant components, while high-purity variants (≥99%) are essential for semiconductor and electronic applications where minimal impurities prevent contamination. Zirconia ceramics stand out for superior toughness (four times that of alumina) and impact resistance, making them ideal for high-load environments like mechanical seals and precision fixtures.
For thermal management scenarios, aluminum nitride ceramics deliver exceptional thermal conductivity (up to 320 W/m·K) paired with electrical insulation, suited for heat-dissipating plates in electronic devices. Silicon nitride offers outstanding thermal shock resistance and high-temperature strength, perfect for furnace components and aerospace structural parts, while silicon carbide excels in corrosion and wear resistance, widely used in chemical processing equipment and abrasive tools. Suppliers like Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. provide comprehensive solutions across all these material types, supporting customers in matching ceramics to their specific industrial needs.
What Are the Core Manufacturing Processes for High-Quality Ceramic Plates?
Producing precision ceramic plates involves a multi-stage process where each step directly impacts final performance, requiring strict control from raw material to finishing.
The process begins with raw material preparation—a critical foundation for quality. High-purity powders (meeting standards for chemical purity, uniform particle size, and phase stability) are selected, then dried to remove moisture, ground to the required fineness (often via ball mills or jet mill), and mixed uniformly to ensure consistent composition. Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd., as a source factory, controls this stage in-house to maintain material integrity.
Molding follows, with techniques chosen based on plate size, thickness, and precision requirements. Dry pressing is suitable for simple, thin plates, while cold isostatic pressing achieves higher density for thicker, load-bearing plates. For complex geometries or tight tolerances, injection molding ensures uniform particle distribution. Sintering is the transformative step: heating the molded blanks to near-melting temperatures fuses powder particles into a dense, strong structure, with sintering temperature and atmosphere strictly controlled to avoid defects like porosity or cracking.
Post-sintering finishing is essential for precision. Surface grinders and CNC machining tools refine the plates to achieve flatness tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm and surface roughness (Ra) below 0.1 μm, critical for applications like semiconductor wafer stages or precision measuring tools. Zhejiang Zhufa’s fully in-house manufacturing capabilities cover this entire workflow, ensuring process consistency from start to finish.
How to Ensure Dimensional Precision and Performance Stability of Ceramic Plates?
Precision and stability are non-negotiable for industrial ceramic plates, relying on rigorous process control and targeted quality inspection throughout manufacturing.
Raw material quality control starts with verifying key parameters: chemical purity (via spectrometry), particle size distribution (using laser diffraction), and moisture content (through thermal analysis) to prevent batch-to-batch variations. During molding, pressure and holding time are monitored in real-time to ensure uniform density, as uneven compaction leads to sintering warpage. Sintering processes use programmable furnaces with precise temperature ramps (±5°C) and inert gas control (for non-oxide ceramics like silicon nitride) to maintain structural integrity.
Finished product testing focuses on two core aspects: dimensional accuracy and performance. Coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and laser flatness testers validate dimensions and flatness, ensuring compliance with design tolerances. Performance tests include hardness (Vickers hardness testing), flexural strength (three-point bending tests), and application-specific evaluations—such as thermal conductivity measurement for aluminum nitride plates or corrosion resistance testing for silicon carbide plates. Zhejiang Zhufa adheres to strict quality control standards across all these stages, guaranteeing the reliability of each ceramic plate.
How to Address Customization Needs for Ceramic Plates Across Industries?
Industrial customers often require non-standard ceramic plates to fit unique equipment designs or operating conditions, making flexible manufacturing and professional support critical to successful customization.
Key customization demands include varied material specifications, non-standard dimensions (from miniature precision plates to large-format panels), special surface treatments (e.g., polished or grooved surfaces), and low-volume prototyping for new product development. Fulfilling these needs requires three capabilities: fully in-house manufacturing to control lead times and quality, direct engineering support to optimize designs for manufacturability, and cross-industry expertise to understand sector-specific requirements.
Zhejiang Zhufa Precision Ceramics Technology Co., Ltd. excels in these areas, offering low-volume & multi-type production to accommodate prototype testing and small-batch orders. Its engineering team collaborates with clients to refine designs—for example, adjusting material thickness for heat dissipation plates or optimizing edge finishes for sealing components—ensuring the final product balances performance, precision, and cost. This customer-centric approach makes it a reliable partner for customized ceramic plate solutions across industries.







 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어