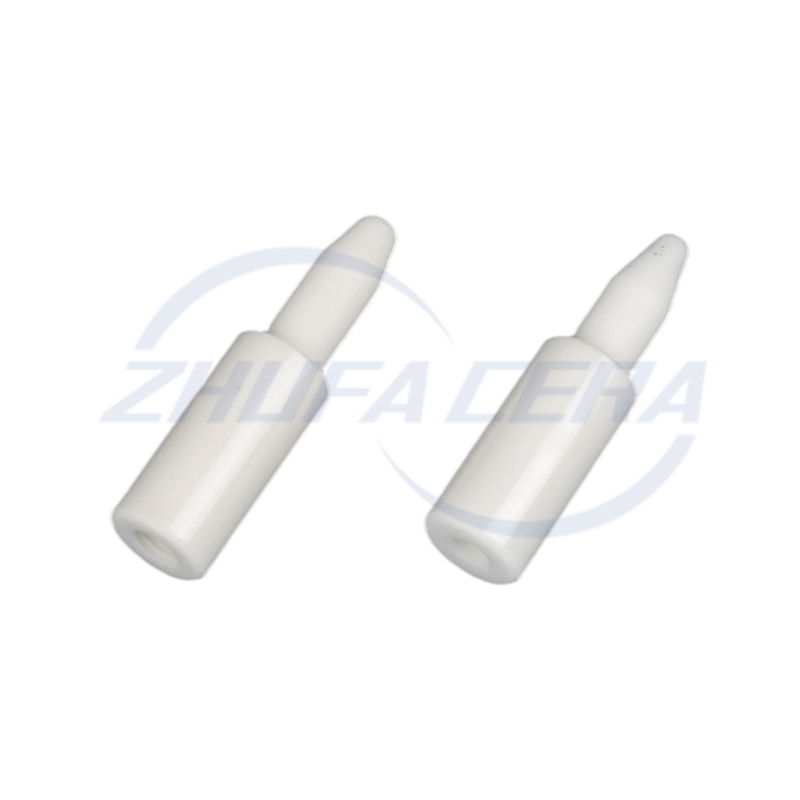
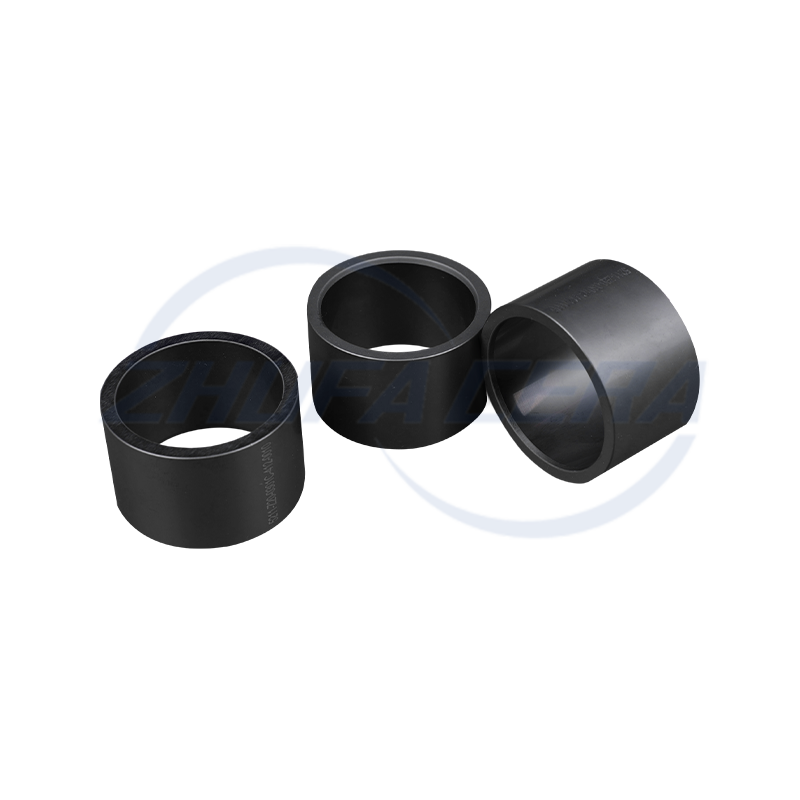
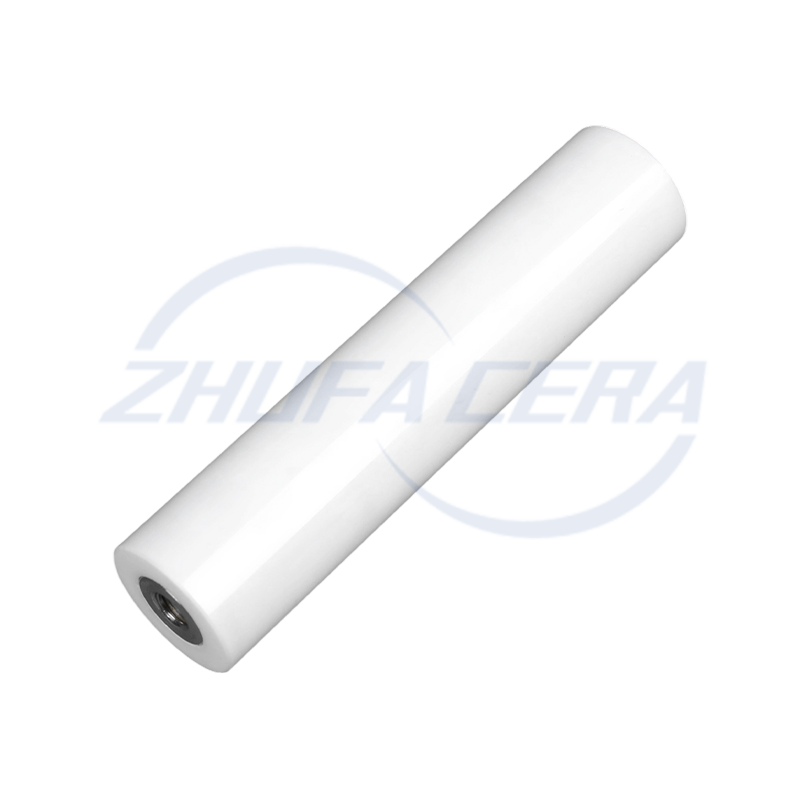
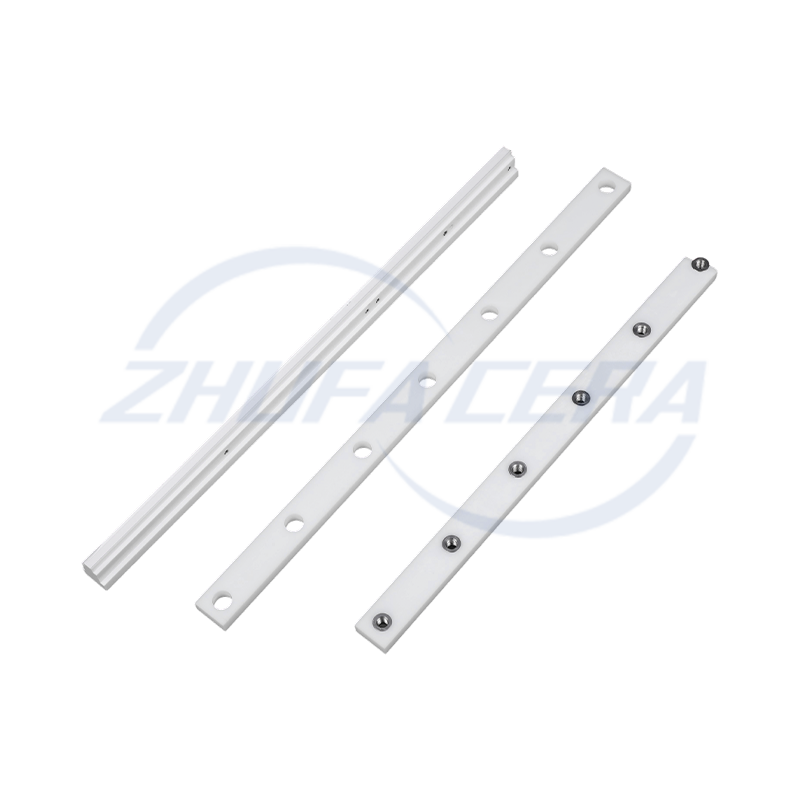
Alumina Ceramic Pin is a high-performance ceramic component with high-purity α-alumina (Al₂O₃) as the main crystal phase. It stands out in the industrial field with its unique material properties. Compared with traditional metal pins or plastic pins, alumina ceramic pins excel in hardness, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and insulation performance. Its Rockwell hardness reaches HRA80-90, second only to diamond, and its wear resistance is 266 times that of manganese steel and 171.5 times that of high-chromium cast iron. At the same time, it can work stably at a high temperature of 1600℃ for a long time and has excellent electrical insulation (resistivity>10¹⁴ Ω·cm). These characteristics make it an ideal substitute for metal parts under harsh working conditions such as high temperature, corrosion, and wear.
Core Features
Superhard and wear-resistant: The hardness of alumina ceramic pins far exceeds that of metal materials, which can effectively resist wear and significantly extend the service life of equipment.
High temperature resistance and thermal stability: melting point up to 2050℃, low thermal expansion coefficient (8-9×10⁻⁶/℃), excellent thermal shock resistance, suitable for high temperature furnace, engine parts and other scenes.
Chemical inertness: resistant to acid, alkali, molten metal corrosion (except hydrofluoric acid and hot concentrated alkali), suitable for chemical reactors, pump body seals and other strong corrosive environments.
Electrical insulation performance: high resistivity and low dielectric constant make it an ideal substrate material for electronic device packaging, ensuring signal transmission stability.
Biocompatibility: high purity alumina ceramics (such as 99.5% Al₂O₃) can be used for artificial joints and dental implants, non-toxic and compatible with human tissue.
Application areas
Electronic industry: as integrated circuit substrates, high-voltage insulators and LED heat sinks, providing insulation support and heat dissipation functions.
Mechanical engineering: used for high-wear parts such as bearings, seals, valves, etc. to reduce equipment downtime maintenance time.
Medical field: manufacturing artificial joint heads and dental implants, reducing the risk of bone dissolution and improving the durability of implants.
Energy and chemical industry: as high-temperature furnace linings and chemical pump mechanical seals, resisting erosion by corrosive media.
Performance advantages
Lightweight: the density is only half of that of steel (3.8-4.0 g/cm³), reducing the load on equipment.
Environmental compliance: no heavy metal pollution, compliant with RoHS standards.
Customized processing: complex shapes can be made through precision molding (such as dry pressing and injection molding) to meet diverse needs.









 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어