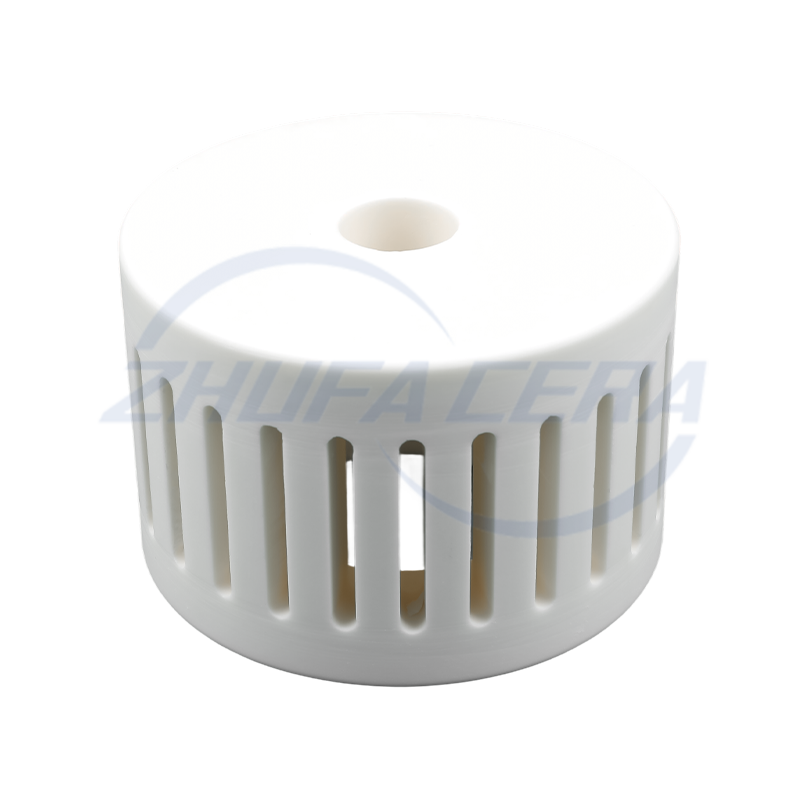
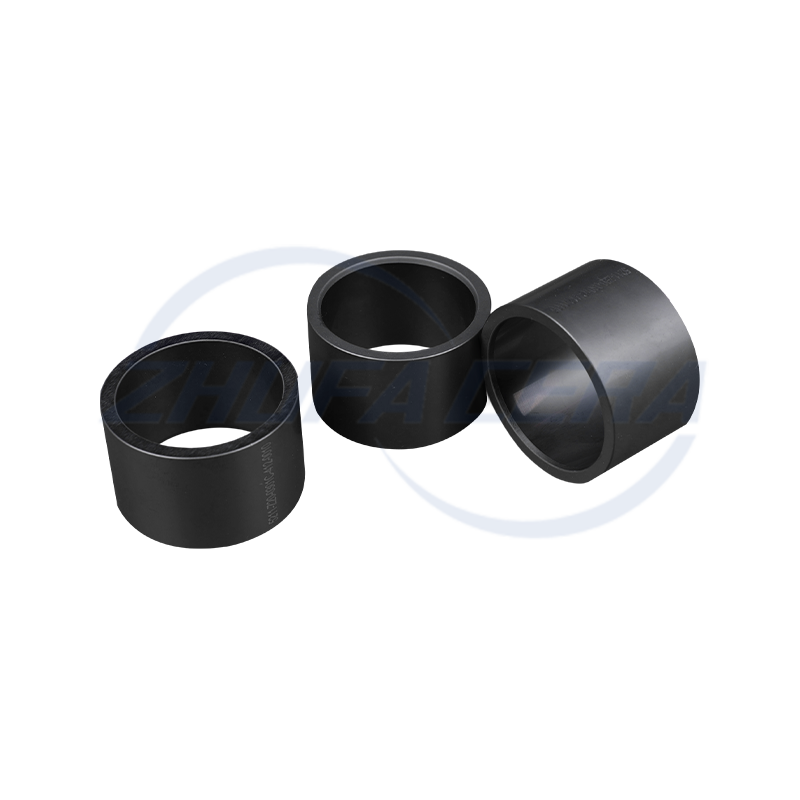
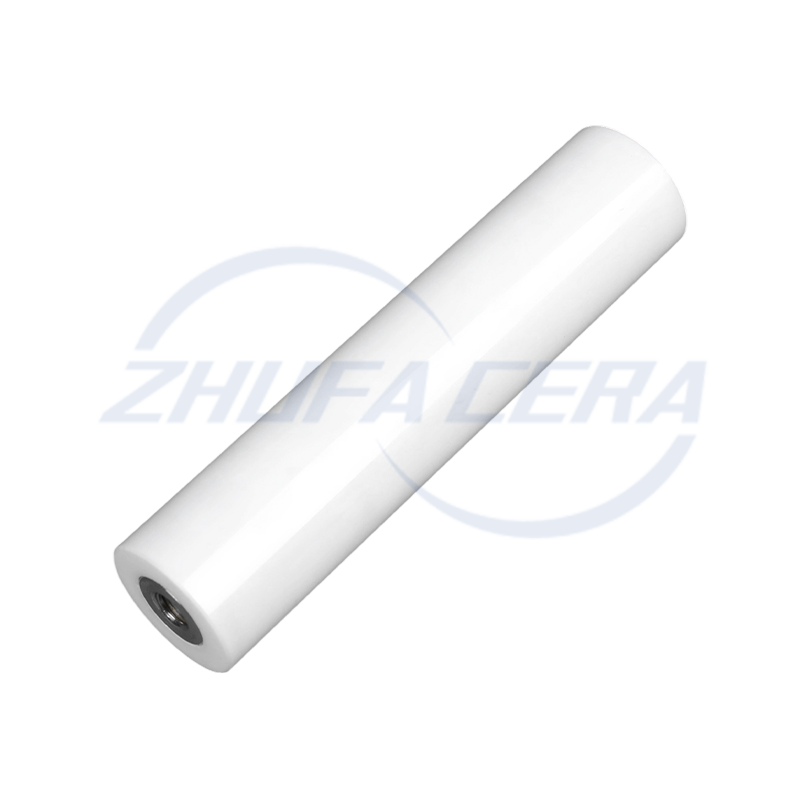
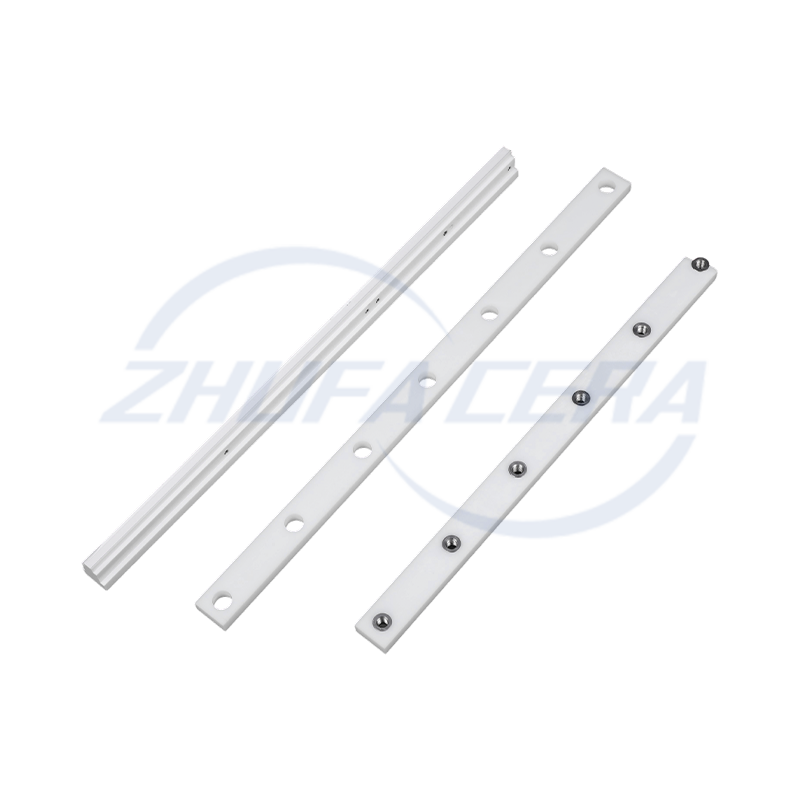
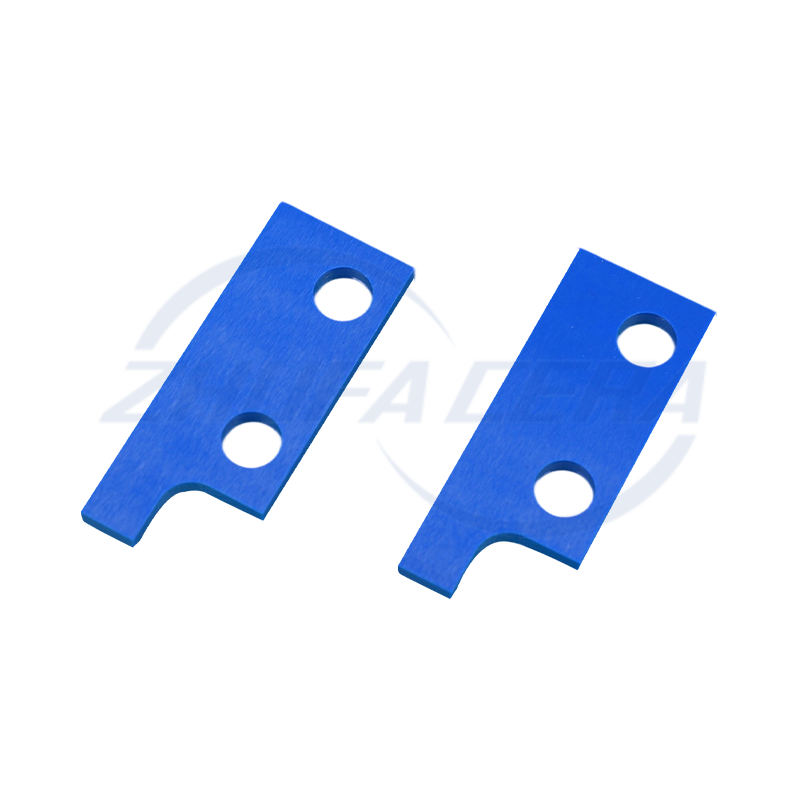
Alumina Ceramic Classifier Wheel is a core precision component used in airflow classifiers and ultrafine powder sorting equipment. Its function is to achieve accurate separation of materials based on the particle size and inertia of the particles. Compared with traditional classifier wheels made of metal or polymer, the core advantage of alumina ceramic classifier wheel lies in the excellent performance of its material itself. It is made of high-purity alumina ceramic sintered by a special process. It has extremely high hardness (Mohs hardness can reach level 9) and excellent wear resistance. It can effectively resist the continuous erosion and wear of powder particles in high-speed airflow, significantly extending the service life of key components. At the same time, the inherent chemical inertness of alumina ceramics gives the product excellent corrosion resistance, enabling it to work stably in acidic, alkaline or other corrosive material environments, while metal wheels are prone to corrosion failure under such conditions. In addition, its low density helps to reduce the inertial load during high-speed rotation. Therefore, the alumina ceramic classifier wheel (Alumina Ceramic Classifier Wheel) shows significant technical advantages in improving classification accuracy, maintaining long-term operating stability, and reducing maintenance frequency and costs caused by wear.
Typical application industries: Widely used in fields that require ultrafine powders or strictly control particle size distribution, including but not limited to:
Non-metallic mineral powders: Ultrafine grading and purification of calcium carbonate, talc, kaolin, quartz powder, mica powder, silicon micropowder, etc.
Advanced ceramics and refractory materials: Fine grading of alumina, zirconium oxide, silicon carbide, silicon nitride powder, etc.
New energy materials: Particle size control of lithium battery positive and negative electrode materials (such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, ternary materials, graphite), photovoltaic materials, etc.
Chemicals and pigments: Grading and depolymerization of fine chemical products, dyes, pigments (such as titanium dioxide).
Biomedicine: Ultrafine processing of pharmaceutical raw materials and excipients (must meet relevant cleanliness and inertness requirements).
Metal powders: Grading of spherical aluminum powder, copper powder, etc.
New materials: Phosphors, catalysts, electronic material powders, etc.









 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى Português
Português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어